Why Should You Use Splunk for Log Analysis ?
Everyone knows that logs play an important role in the IT industry. Logs are used for various purposes such as IT operations, system and application monitoring, business analytics, security and compliance and much more.
Having a centralized logging system makes life easy for developers especially when there is a need to troubleshoot the application, detect issues, secure the application due to unexpected hits on services or review the performance of the application, etc. Some of the great features of a centralized logging system are its low-cost maintenance, easy logs searching, graphical UI etc.
Splunk is centralized logs analysis tool for machine generated data, unstructured/structured and complex multi-line data which provides the following features such as Easy Search/Navigate, Real-Time Visibility, Historical Analytics, Reports, Alerts, Dashboards and Visualization.
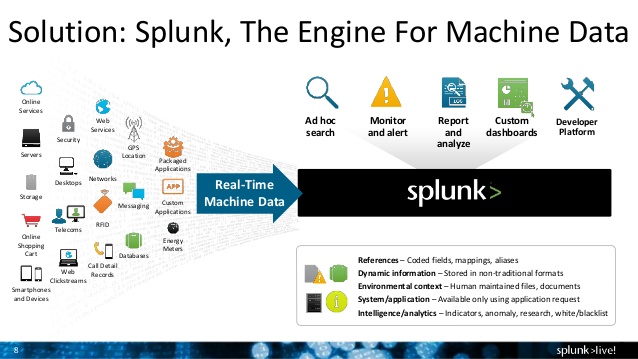
1) Advantages of Splunk and why to use it ?
- Analyzes the aggregate of logs from a big service cluster
- Finds real-time logs and with faster speed
- Generates report and alerts for the desired search
- Provides enhanced GUI and real-time visibility in dashboard in various formats
- Provides quick results by reducing the time to troubleshoot and resolve issues
- Works like a monitoring, reporting and analysis tool and provides insights
- Does not require other dependent services (like database)
- Requires minimum HW resources
- Easy to setup and low-cost maintenance
- Accepts any data type including .csv, JSON log formats etc.
- Monitors AWS infrastructure
- Uploads and indexes log data from a local PC to Splunk directly
2) Versions of Splunk
Splunk comes in two versions – Free and Enterprise edition.
- Free Version: The Splunk Free license is for the low volume of logs, it provides max 500 MB of indexing per day.
- Enterprises Version: The Splunk Enterprise and Splunk Cloud licenses supports multi-user, distributed deployments. It also offers additional capabilities to support higer data volumes including alerting, role-based security, single sign-on, scheduled PDF delivery, clustering, premium Splunk apps, etc.
For more details – https://www.splunk.com/en_us/products/splunk-enterprise/free-vs-enterprise.html
3) How to setup Splunk for your infrastructure?
Splunk works on the client-server model. Splunk Forwarder is used to collect the machine generated data from client side and forward to Splunk server.
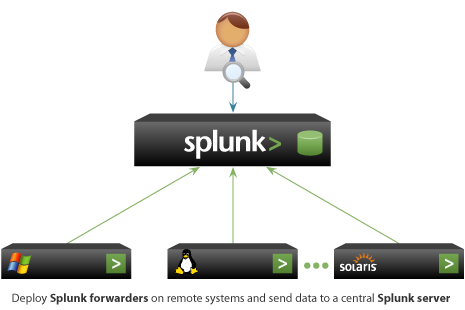
3.1: Setup a Splunk Servers
3.1.1: Download and install Splunk
$ cd /opt $ wget -O splunk-6.5.1-f74036626f0c-Linux-x86_64.tgz 'https://www.splunk.com/bin/splunk/DownloadActivityServlet?architecture=x86_64&platform=linux&version=6.5.1&product=splunk&filename=splunk-6.5.1-f74036626f0c-Linux-x86_64.tgz&wget=true' $ tar -xvzf splunk-6.5.1-f74036626f0c-Linux-x86_64.tgz $ /opt/splunk/bin/splunk start
3.1.2: Enable the receiving port to get logs from Splunk Forwarder.
We can do this from GUI and CLI as well. Port 9997 is default and it can be changed
$ /opt/splunk/bin/splunk enable listen 9997
Open browser and type http://splunk-server-ip:8000 to access Splunk web console.
3.2: Setup Splunk Forwarder
3.2.1: Download and install Splunk Forwarder
$ cd /opt $ wget -O splunkforwarder-6.5.1-f74036626f0c-Linux-x86_64.tgz 'https://www.splunk.com/bin/splunk/DownloadActivityServlet?architecture=x86_64&platform=linux&version=6.5.1&product=universalforwarder&filename=splunkforwarder-6.5.1-f74036626f0c-Linux-x86_64.tgz&wget=true' $ tar -xvzf splunkforwarder-6.5.1-f74036626f0c-Linux-x86_64.tgz $ /opt/splunkforwarder/bin/splunk start
3.2.2: – Add the logs in Splunk Forwarder
$ vim /opt/splunkforwarder/etc/system/local/inputs.conf [default] host = <HOSTAME OF CLIENT> [monitor:/var/log/secure.log] [monitor:<other logs path>]
$ vim /opt/splunkforwarder/etc/system/local/outputs.conf [tcpout] defaultGroup = default-autolb-group [tcpout:default-autolb-group] server = <splunk-server-ip>:9997 [tcpout-server://splunk-server-ip:9997]




I know this web page gives quality dependent articles or reviews and extra information, is there any other web site which gives these kinds of information in quality?