Blockchain And Healthcare
The Blockchain Database is a distributed database that stores transactional data in the form of time as a “block” of recorded data and transactional data is unchanged. Nodes are the members of a Blockchain network that authenticate transactions. Blockchain technology allows different types of nodes to enter the Blockchain network, using specialized software such as Ethereum. The private and public key pair is transliterally linked to one direction only. The encrypted message using the private key can only be read by nodes with the public key attached to the private key, allowing users to access or read encrypted messages or data.
Any action on the Blockchain is the work of the network, so the hacker must modify the same data on all the nodes of the network to convert any transaction data. This basically means hacking all of the network’s systems at once, which is practically impossible. Blockchain is based on consensus; each transaction requires permission from more than half the participants or nodes before execution. Every transaction on a Blockchain is public, but access to the contents of each transaction may be limited depending on the sensitivity of the transaction. Today Blockchain has applications in every sector – Finance, Healthcare, Economics, Legal, etc. Some examples in the field of healthcare where the Blockchain can be used: EHRs, clinical trials to eliminate manufacturer-to-consumer drug traceability, fraudulent data changes and interoperability.
Blockchain provides us with an excellent opportunity to tackle the challenges of the healthcare industry today, including interoperability, security, integrity, permeability and universal access.
Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain has attracted the attention of markets for its data management capabilities with respect to decentralization and security with distributed data technology. With its relatively successful implementation in the financial sector, various industries are now realizing its benefits and finding Blockchain potential in their respective domains. Healthcare is an industry that describes the benefits of Blockchain. There are many opportunities in health care, and Blockchain that can help improve the interoperability and confidentiality of patient health data. Some important health care applications are discussed in this article.
1. Blockchain For Electrical Health Records (EHR)
The ideal scenario with EHRs is to maintain a lifelong medical record and make it available to physicians, lab technicians, etc., and to the timely care team. In the current implementation of the EHR, patient data is stored in various organizations over the lifetime of the patient. Patient’s medical records, such as Ofc’s problems, are recorded by doctors, and they retaliate even after the patient receives treatment. In Blockchain implementation, a patient maintains a medical record and is granted access to doctors on a “smart contract” basis.
2. Clinical Research and Blockchain
Although much progress has been made in transferring medical data from paper to digital records, the healthcare industry is still working through patient data sharing issues among providers and organizations. In their lifetime, patients may travel to cities, change health plans, and change their health care providers for treatment. Most of their detailed medical records are in the pit with a personal facility or provider. In addition, each medical unit must save patient data in its own storage structure and semantics. This leads to data sharing.
These barriers are partly due to the nature of the data (protected health information) or the information being blocked during the exchange. This is not only effective in the treatment of patients in many institutions, but also in the field of clinical research with real-life data to investigate and test their hypotheses in real-world scenarios.
3. Drugs Supply Management and Blockchain
One of the major challenges in the industry is the transparency and security aspect of supply chain management. Pharma companies lose millions annually due to drugs. Pharma companies deal with products that directly impact the lives of their customers, so the efficiency and safety of the product is vital. There are several stages in the product’s journey from manufacturer to consumer: transportation, maintenance, storage, re-distribution, retail. Things can go wrong at this stage, from simple human error to malicious intent. In the traditional system, this problem is difficult to identify because participants in the supply chain can usually maintain their own records and share their information, usually one level up and one level down in the chain. Further, if these records are paper-based, they have drawbacks. These factors delay research to identify problems along the factor supply chain.
Blockchain helps to solve supply chain problems by providing a shared supply chain among all stakeholders in the supply chain. At every stage of the supply chain, the records in the Blockchain are immutable, permanent and decentralized. This eliminates the vulnerability of introducing errors or frauds. Duplicate drugs are minimized by maintaining a chain of custody logs that allows companies to track every step of the supply chain at the individual drug level or product level. With the Blockchain system, the end user also now has all the information from product creation to consumption.
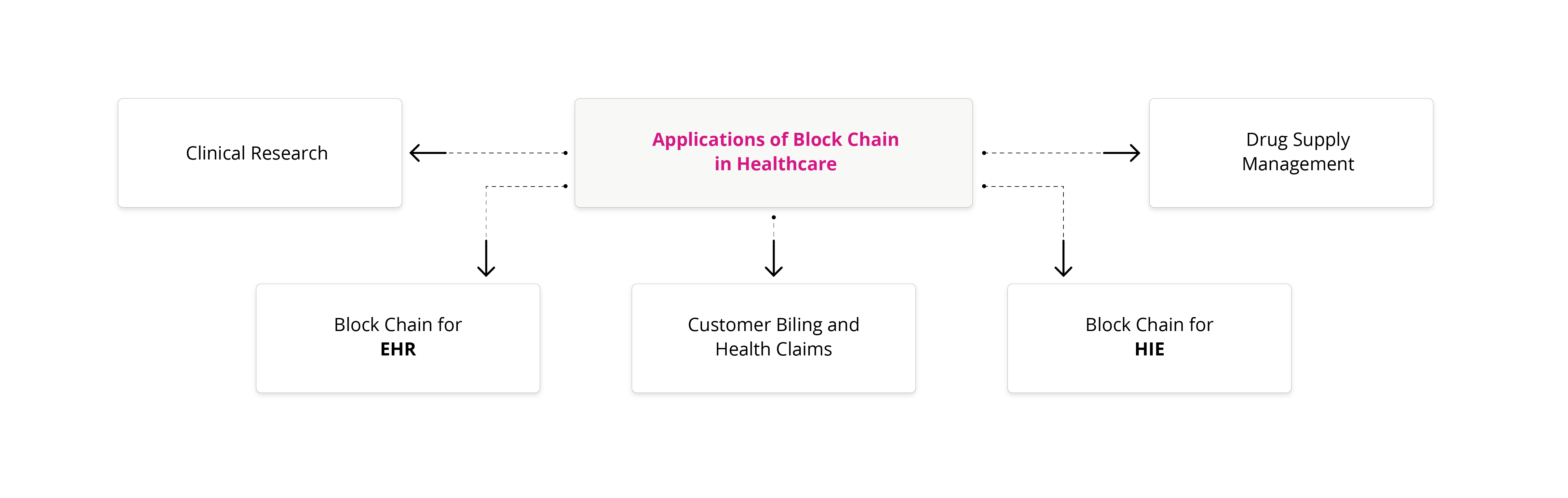
4. Blockchain in Consumer Billing and Healthcare
One of the pitfalls in health care should be eliminated and avoided are fraudulent claims and billing. Medical billing related fraud is still very common in the healthcare space. Most common health care scams are providers that claim fees for non-performing services, over-charge actual services, and maintain services. Misrepresentation of non-covered medical services for inpatient medical conditions, receipt of claims money, and financial losses are most common.
Many stakeholders are involved in verifying and postponing claim information, making sure there is a very short time frame for claim processing, and reducing administrative costs for providers and payers. Communication between the parties involved in claim processing is behind walls in the typical process of claim processing. The Blockchain system helps to mitigate these challenges during claims settlement and payment processing operations. The Blockchain solution can automate the required workflow, and then all parties involved can share a single copy of contracts and billing information.
5. Blockchain Application in HIE
The primary goal of the HIE is to disseminate health care data beyond geographical and institutional boundaries to provide an effective and secure delivery mechanism. With a universal partnership approach, there are many factors that need to be considered,
- Security – Data privacy is of utmost importance, as is the failure to secure patient data, as well as financial and legal implications
- Infrastructure – Traditionally data sharing requires a centralized data source, which increases security risk footprint and requires reliance on a single centralized authority
- Differentiation – All required parties must share the data so that it can understand the structure and meaning
On the Blockchain, all data is encrypted with the participant’s private key on the network. Only a few nodes or participants can access the information by sharing the public key of the sending participant, thereby ensuring confidentiality and confidentiality.
In traditional HIEs, data from different users of the network is stored in their personal storage systems and sent to the HIE periodically. This is a centralized storage system, where centralized storage failures endanger many patients’ medical record updates. As data per patient grows from different sources, such as Webbers, doctors, and lab reports, there is pressure on HIEs to support the diversity of infrastructure and data sources.
In Blockchain technology architecture, each patient controls ownership of medical records in contrast to traditional architectures, where the central authority accesses and distributes data over the network.
Medical record access is only granted to limited health care organizations (individuals or organizations). Data shared across the Blockchain network allows real-time updates to all healthcare organizations. Secure access to the patient’s 360 data via a distributed ledger is possible. Data duplicates are minimized because only one copy of the data is available to everyone.

