Functional Interface for Lambda expressions : Java 8
As we already know that Lambda Expressions are used to support functional programming in Java. The default behaviour of Lambda expressions is to accept only those interfaces as reference variables which have only one abstract method. We call such interfaces Functional Interfaces. You could also name them as SAM, i.e., Single Abstract Method interfaces.
Java 8 provides an annotation Functional Interface that strictly ensures that at compile time, the interface has only one abstract method. If there is an additional abstract method present, the program shows an error in the interface.
Let us understand it through an example. Suppose we have to write a program to print “Hello India!” A simple implementation using Lambda expressions could be:
[code lang=”java”]
public class FunctionalInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Printer printer = ()-> System.out.println("Hello India!");
printer.print();
}
}
interface Printer{
abstract void print();
}
[/code]
Above will successfully print the desired output:

Now if a new developer tries to add another abstract method to the interface, he/she could easily add it as is allowed by default implementation. Though the code will break at the compile time wherever we use the interface as a reference variable for a Lambda expression, it would never give a hint to the developer before to compiling the program about the attempt made to modify a functional interface. Hence, to show an error at the interface, we could add an annotation FunctionalInterface explicitly. This annotation ensures that you are not adding an extra abstract method to a functional interface.
Hence, there is one thing to learn that functional interfaces have a different purpose and usage even though they follow same architecture as regular interfaces.
So with annotation, the code mentioned above looks like as shown below and IDE shows error at the interface itself.
[code lang=”java”]
public class FunctionalInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Printer printer = ()-> System.out.println("Hello India!");
printer.print();
}
}
@java.lang.FunctionalInterface
interface Printer{
abstract void print();
}
[/code]
I am adding a screenshot rather than code snippet to show how IDE shows the error when we add another abstract method to the interface.
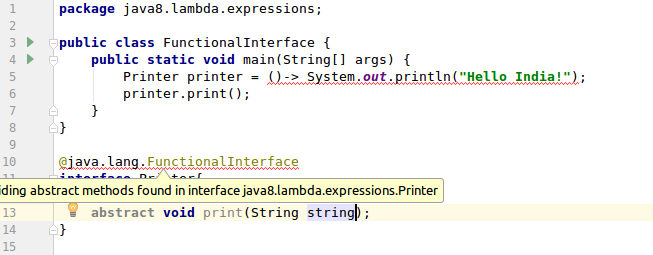
Notice that an error occurs around interface name after the addition of the abstract method. Hence, the annotation is more of a marker telling, “Hey! This is a functional interface and has a particular purpose”.
Also, Java 8 provides a library under java.util.function package under rt.jar that contains lots of useful functional interfaces. I would be talking about those in more detail in my next blog.
Hope, this helps to understand a different aspect of functional programming & Lambda expressions with Java 8.



