LLM Fine-Tuning Explained: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How It Works
Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude are very powerful. They can answer questions, write text, generate code, and help in many tasks. However, these models are trained on very general data from the internet. Because of this, they may not always understand your specific business, domain, or writing style.
This is where LLM fine-tuning becomes useful.
Fine-tuning means taking an already trained model and teaching it using your own data. You are not building a new model from zero. Instead, you are slightly adjusting an existing model so it gives better and more accurate answers for your use case.
In this blog, we will explain what LLM fine-tuning is, why it is important, and how it works in a simple way. We will also help you understand when fine-tuning is needed and when other approaches like prompt engineering or RAG might be a better choice.
Fine-tuning means teaching an already trained AI model to behave better for a specific task.
Think of it like this:
- A base LLM is like a college graduate
- Fine-tuning is on-the-job training
The model already knows language, grammar, and general knowledge. Fine-tuning helps it:
- Speak in a specific tone
- Follow company rules
- Answer domain-specific questions
- Format responses correctly
You’re not training from scratch.
You’re adjusting an existing model using your own examples.
Why Do We Need Fine-Tuning?
- Pre-trained LLMs are general-purpose and may not understand your specific domain or business rules
- Fine-tuning helps the model give more accurate and consistent answers
- It allows the model to follow a specific tone, format, or behavior required for real-world applications
Real-World Examples
- HR chatbot trained to answer questions based on company policies
- Customer support bot trained using past support tickets for better replies
- Legal assistant that responds in a formal and professional language
- Healthcare assistant that uses medical terms and phrasing
- Sales assistant that follows the company’s sales pitch and tone
How Does Fine-Tuning Work?
- Start with a pre-trained LLM (already trained on large data)
- Prepare your own examples (questions and correct answers)
- Train the model on this data so it learns your style and rules
- Test the model and improve it step by step
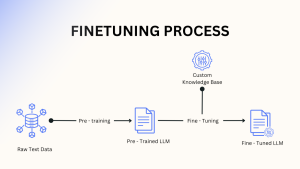
LLM fine-tuning
At a high level, fine-tuning has three simple steps.
Step 1: Prepare Training Data
- Collect examples like questions and correct answers or input and expected output based on your use case.
Step 2: Train (Adjust) the Model
- Train the existing model using this data so it learns your rules, tone, and domain.
Step 3: Use the Fine-Tuned Model
- Use the fine-tuned model in your application to get more accurate and consistent results.
Different Ways to Fine-Tune an LLM:
1. Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)
In this method, the model is trained using clear examples. Each example has an input and the correct
Output.
This helps the model learn what the right answer looks like for your use case.
Example:
Question → Correct answer pairs for customer support.
2. Instruction Fine-Tuning
Here, the model is trained to understand and follow instructions instead of just answering questions.
This makes the model better at handling different tasks like summarizing, explaining, or generating content.
Example:
“Explain this policy in simple words” or “Write a formal email.”
3. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (LoRA / Adapters)
This approach updates only a small part of the model instead of the full model.
It is faster, cheaper, and uses less memory, while still giving good results.
Example:
Fine-tuning a large model for a specific task without retraining everything.
Fine-Tuning vs RAG:
Fine-Tuning
-
- Changes the model’s behavior by training it on your data
- Best when you need consistent tone, rules, or style
- Knowledge is fixed after training
- More effort and cost compared to prompting
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
-
- Does not change the model
- Fetches information from external documents at runtime
- Best for up-to-date or frequently changing data
- Easier to update—just change the documents
Simple Rule:
-
- Use fine-tuning for how the model should behave
- Use RAG for what information the model should know
Conclusion
LLM fine-tuning helps make a language model more useful for a specific task or business. It improves accuracy, consistency, and tone by teaching the model with your own data.
Fine-tuning is best when you want the model to behave in a certain way, while RAG is better when you need the model to use updated or large amounts of information. In many real-world cases, both can be used together.
By understanding when and how to fine-tune, you can choose the right approach and build better, more reliable AI applications.

