Essential SQL Queries Every Tester Should Know
Introduction to SQL:
When you’re just starting with SQL, it’s easy to get overwhelmed by syntax and theory. But here’s the truth: most professionals – whether they’re data analysts, marketers, or product managers – use a small set of SQL queries over and over to get real work done. You don’t need to learn everything at once.
In today’s data-driven world, almost every application relies on databases to store and manage information. SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language used to interact with these databases. It allows users to create, retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently and accurately. From powering simple applications to supporting complex enterprise systems, SQL plays a vital role in handling structured data. This blog explores the fundamentals of SQL, its importance, and how it is widely used across different roles such as development, data analysis, and quality assurance.
In this blog, we will explore:
- Why Learn SQL?
- What is SQL?
- Basic SQL Commands
- Aggregation Functions
- Types of Joins
- Real World Usage of SQL
- Conclusion
Why Learn SQL?
- Universality – Almost every application uses a database.
- High demand skill – Data analysts, developers, and testers all benefit from SQL knowledge.
- Simplicity – SQL is easy to learn compared to other programming languages.
- Powerful – With just a few commands, you can manage millions of rows of data.
- Testers use SQL for backend DB validation:
- CRUD Operations Validation: Ensure Create, Read, Update, and Delete operations are working as expected.
- Cross-Table Validation: Use JOIN queries to confirm data consistency across related tables.
Example:
If a user updates their mobile number in the app, a tester will run an SQL query like below, to confirm that the updated value is correctly reflected in the database.
SELECT mobile_number FROM users WHERE user_id = 12345;
What is SQL?
Before starting off with SQL, let us understand about Database and DBMS:
1.Database: Database is a collection of data that allows data to be stored, retrieved ,managed and updated efficiently.
2.DBMS:Software that manage the databases is known as DBMS. It provides tools to create, update, read, delete the data and ensure security. Few examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL , Oracle etc.
In order to interact with the relational Databases(databases where data is stored in rows and tables), SQL is used. It is a query language which is used to store and retrieve the data from a database.
Consider we have following CUSTOMERS table which stores customer’s ID, Name, Age, Salary, City and Country − For example, if we want to list down all the customers from USA , then following will be the SQL query
SELECT * FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE country = ‘USA’;
| ID | Name | Age | Salary | City | Country |
| 1 | Ram | 32 | 1000 | Utica | USA |
| 2 | Mohit | 40 | 4000 | New York | USA |
| 3 | Sumit | 45 | 4500 | Muscat | Oman |
| 4 | Karan | 25 | 2500 | Agra | India |
This will produce the following result:
| ID | Name | Age | Salary | City | Country |
| 1 | Ram | 32 | 1000 | Utica | USA |
| 2 | Mohit | 40 | 4000 | New York | USA |
Fundamental SQL Commands:
1) Data Definition Language (DDL): DDL (Data Definition Language) consists of SQL commands that can be used for defining, altering and deleting database structures such as tables, indexes and schemas. It simply deals with descriptions of the database schema and is used to create and modify the structure of database objects in the database.
- CREATE TABLE … to define new tables
- ALTER TABLE … to change existing tables
- DROP TABLE … to remove tables
- TRUNCATE TABLE … to quickly delete all rows
2) Data Manipulation Language (DML):DML(Data Manipulation Language) commands are used to manipulate the data stored in database tables. With DML, you can insert new records, update existing ones, delete unwanted data or retrieve information.
- SELECT … to fetch records
- INSERT INTO … to add new records
- UPDATE … to modify existing records
- DELETE FROM … to remove records
3) Data Control Language (DCL): DCL (Data Control Language) includes commands such as GRANT and REVOKE which mainly deal with the rights, permissions and other controls of the database system. These commands are used to control access to data in the database by granting or revoking permissions.
- GRANT … to give users specific rights
- REVOKE … to remove those rights
Basic SQL Commands Syntax
Here are some of the most common SQL operations:
1.Create a Table:
CREATE TABLE Employees (
EmployeeID INT PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName VARCHAR(50),
LastName VARCHAR(50),
Department VARCHAR(50),
Salary DECIMAL(10,2)
);
Here Employees refers to table name.
EmployeeID:Columnn1
FirstName:Column2
LastName:Column3
Salary:Column4
2. Insert Data:
INSERT INTO Employees (EmployeeID, FirstName, LastName, Department, Salary)
VALUES (1, ‘Joh’, ‘Do’, ‘IT’, 60000.00);
3. Select Data:
SELECT FirstName, LastName, Department
FROM Employees
WHERE Department = ‘IT’;
4.Update Data:
UPDATE Employees
SET Salary = 65000.00
WHERE EmployeeID = 1;
5.Delete Data
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeID = 1;
Filtering and Sorting Data:
SQL offers powerful ways to filter and organize results:
- WHERE: Restricts results based on conditions, e.g., SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > 1000.
- ORDER BY: Sorts results by one or more columns, e.g., ORDER BY price DESC for descending price order.
- LIMIT: Restricts the number of results, e.g., LIMIT 5 for only five records.
Aggregation and Grouping:
SQL makes it easy to summarize data with aggregate functions:
- SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX: Calculate totals, averages, minimums, maximums.
- COUNT: Tallies the number of results
- Grouping is achieved via GROUP BY, for example:
SELECT country, COUNT(*) FROM CUSTOMERS GROUP BY country;
This counts the number of customers per country
Working with Joins:
Joins are used to combine two or more related tables based on a related column.
Uses of Joins:
1.Combine related data
2.Retrieve data from multiple tables
3.Perform aggregation on data from multiple tables
4.Filter data from multiple tables
Types of SQL JOINs:
INNER JOIN: The INNER JOIN keyword selects all rows from both the tables as long as the condition is satisfied. This keyword will create the result set by combining all rows from both the tables where the condition satisfies i.e value of the common field will be the same.
LEFT JOIN: A LEFT JOIN returns all rows from the left table, along with matching rows from the right table. If there is no match, NULL values are returned for columns from the right table. LEFT JOIN is also known as LEFT OUTER JOIN.
RIGHT JOIN: RIGHT JOIN returns all the rows of the table on the right side of the join and matching rows for the table on the left side of the join. It is very similar to LEFT JOIN for the rows for which there is no matching row on the left side, the result-set will contain null. RIGHT JOIN is also known as RIGHT OUTER JOIN.
FULL JOIN: FULL JOIN creates the result-set by combining results of both LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN. The result-set will contain all the rows from both tables. For the rows for which there is no matching, the result-set will contain NULL values.
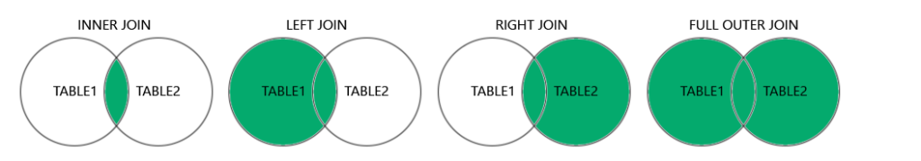
Types of SQL JOINs
Real-World Applications of SQL:
1)Data Science: Data science professionals use SQL to quickly analyze data, extract data from large databases, and generate new insights. Data Scientists use business data to create predictive models ; this data must typically be extracted using SQL from a relational database.Data Analysts use SQL to analyze data, and the insights obtained from data analysis can facilitate decision-making.
2)Cybersecurity: SQL is one of the best cybersecurity database languages, as it is practically impossible to prevent a database attack without using SQL. Professionals in the field of cybersecurity must have a solid grasp of SQL and database operations. Ethical hackers or attackers can use SQL Injections like SQLdict to find other users’ login details within the database. SQL allows cybersecurity professionals to select which data to export from the database. A SQL Injection vulnerability may also allow a professional to view all the data on a database server.
3)Social Media: Social media sites like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and others have large customer bases and vast daily bandwidth usage. Social media users regularly share photos and posts, requiring regular data monitoring on these platforms using SQL and continuous display of content to millions of users. When a user uploads content, popular apps like Instagram and Snapchat use SQL to update the app’s database with the most recent information.
4)Marketing: Customer behavior analysis, customer segmentation, marketing channel analysis, etc., are just a few marketing-related areas where SQL is beneficial. Marketing analysts commonly use SQL to comprehend user data and determine crucial marketing metrics like customer lifetime value (CLV), cost per acquisition (CAC), etc. SQL also helps to obtain in-depth user data within company databases and perform complex queries on Google Analytics data, etc.
Conclusion:
Learning SQL provides a solid foundation for any data-driven work. It helps you interact with databases efficiently. It can be used for the database testing for QA. As applications become increasingly data-driven, SQL continues to be an essential skill that enhances the efficiency, confidence, and overall impact of a QA professional.

