How GenAI Is Transforming Data Engineering
Introduction
Data engineering, once dominated by manual coding, SQL development, and repetitive operational tasks, is entering a new era. With Generative AI (GenAI), data teams are automating ingestion workflows, accelerating data modeling, writing code faster, improving quality checks, and generating documentation instantly.
GenAI isn’t just an add-on—it is fundamentally transforming how modern data platforms are designed, monitored, and optimized.
From speeding up data quality checks to auto-generating SQL, documentation, and even entire data pipelines, GenAI is transforming both the productivity and capability of data engineering teams.
In this blog, we explore how GenAI is reshaping data engineering with real industry examples, practical use cases, tools you can adopt today, and what the future looks like for modern data teams.
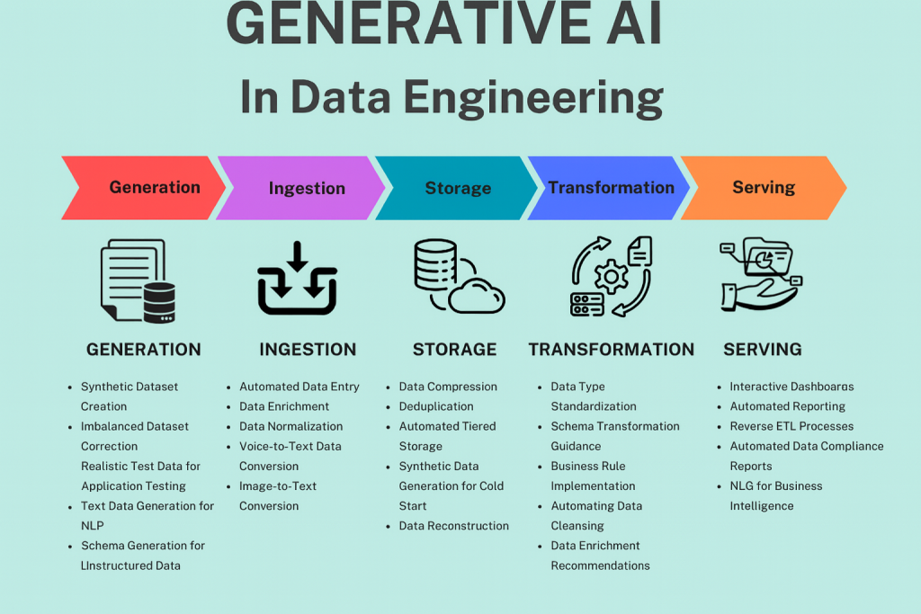
Generative AI
Why GenAI Matters for Data Engineering
Historically, data engineering has involved repetitive manual tasks:
- Writing boilerplate SQL and PySpark code
- Handling schema drifts
- Creating documentation
- Troubleshooting pipeline failures
- Building lineage and impact analysis
- Standardizing quality checks
GenAI automates most of these, while also enabling intelligent decision-making in pipelines. Instead of reacting to failures, pipelines adapt proactively using metadata, execution history, and runtime signals.
- Learns from metadata, data dictionaries, SQL workloads, and lineage graphs
- Produces human-like explanations and optimized code
- Predicts issues before they occur
- Makes pipelines self-healing or auto-generated
This means data teams can finally focus more on architecture, governance, and business value—rather than plumbing.
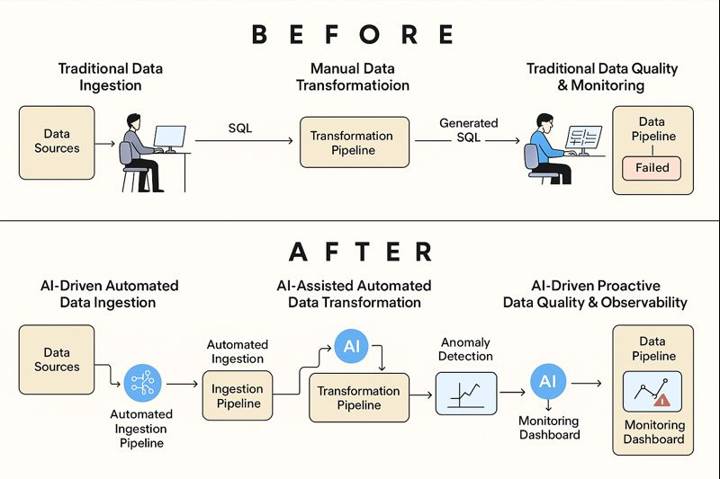
DE Before VS After
How GenAI Is Transforming Each Layer of Data Engineering
1. GenAI in Data Ingestion & Integration
- Auto-generates ingestion scripts (Kafka, S3, APIs)
- Detects schema changes and suggests corrections
- Recommends batch vs streaming based on data patterns
In real production systems, GenAI continuously monitors ingestion metadata. For example, when a new column such as device_type appears in a Kafka topic, the AI detects schema drift, updates the Bronze Delta schema, and regenerates ingestion logic—without breaking downstream Silver or Gold tables.
Mini PySpark (Auto-Generated Ingestion)
df = spark.readStream.format("kafka").load()
df = schema_evolver.apply(df)
df.writeStream.table("bronze_transactions")
Example: A FinTech firm integrated GenAI into their Kafka streaming architecture. GenAI monitored logs, correlated ingestion spikes with transaction metadata, and flagged anomalies as potential fraud—reducing fraud leakage by 35%.
Before GenAI (Data Ingestion): Manual pipeline creation—writing connectors, handling schema changes, maintaining ingestion scripts, and troubleshooting failures.
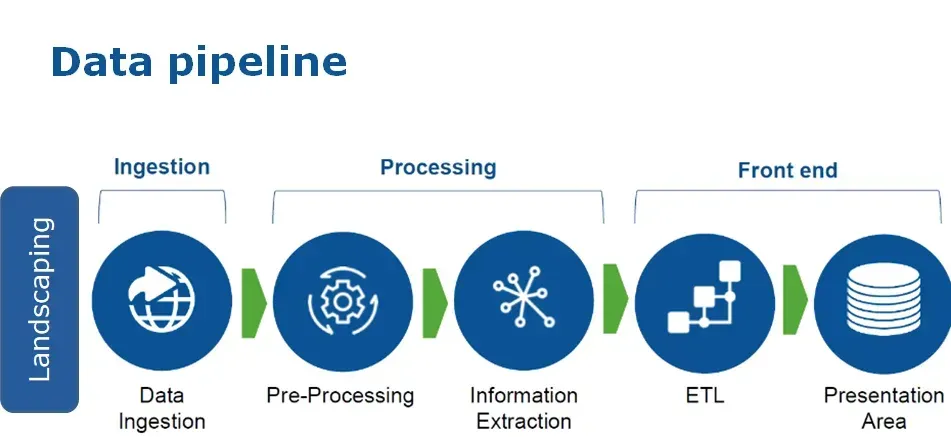
Data Pipeline Architecture
After GenAI (Data Ingestion): Ingestion pipelines are auto-generated, self-optimizing, and schema-aware. AI tools detect anomalies, suggest pipeline fixes, and generate ingestion code instantly.
AI Data Pipeline
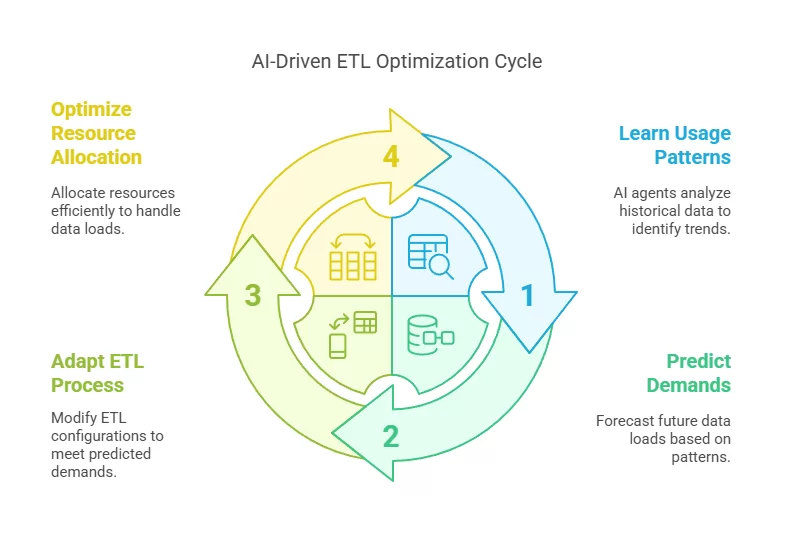
AI Driven ETL Optimization Cycle
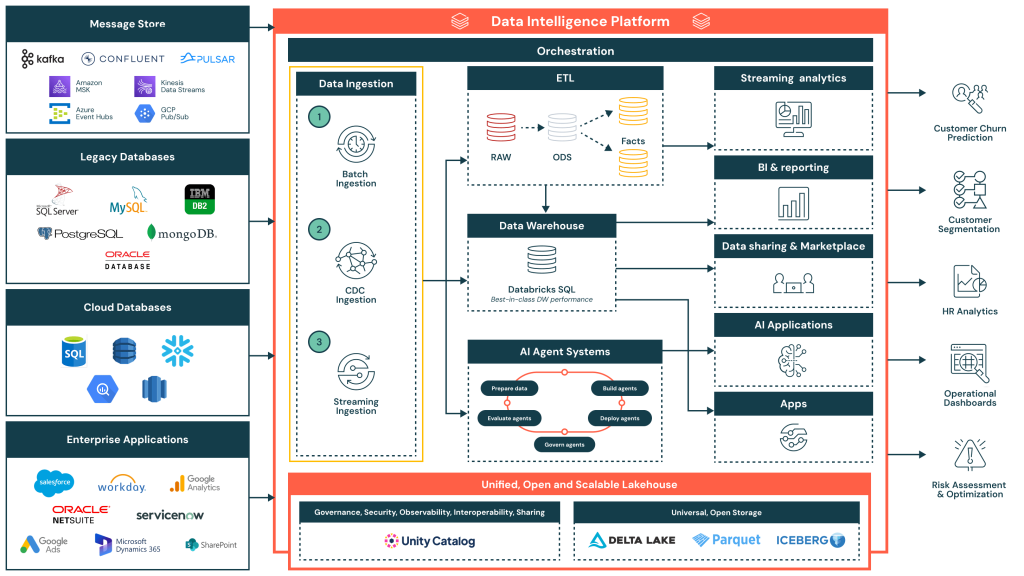
Data Ingestion Reference Architecture
2. GenAI for Data Transformation (SQL, PySpark, ETL/ELT)
GenAI significantly reduces development time by generating:
- PySpark code for transformations
- SQL for joins, aggregations, and window functions
- Complex DAX or dbt Jinja macros
Instead of writing transformations line-by-line, engineers describe intent such as “calculate a 7-day rolling revenue per customer.” GenAI then generates optimized SQL and Spark code with correct partitioning and caching strategies.
Mini SQL Example
SELECT customer_id,
SUM(amount) AS total_revenue,
AVG(amount) OVER (
PARTITION BY customer_id
ORDER BY order_date
ROWS BETWEEN 6 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW
) AS rolling_7d_avg
FROM transactions;
Before GenAI: Engineers wrote transformations manually, taking hours.
After GenAI: Tools like Databricks Assistant generate optimized transformations in seconds.
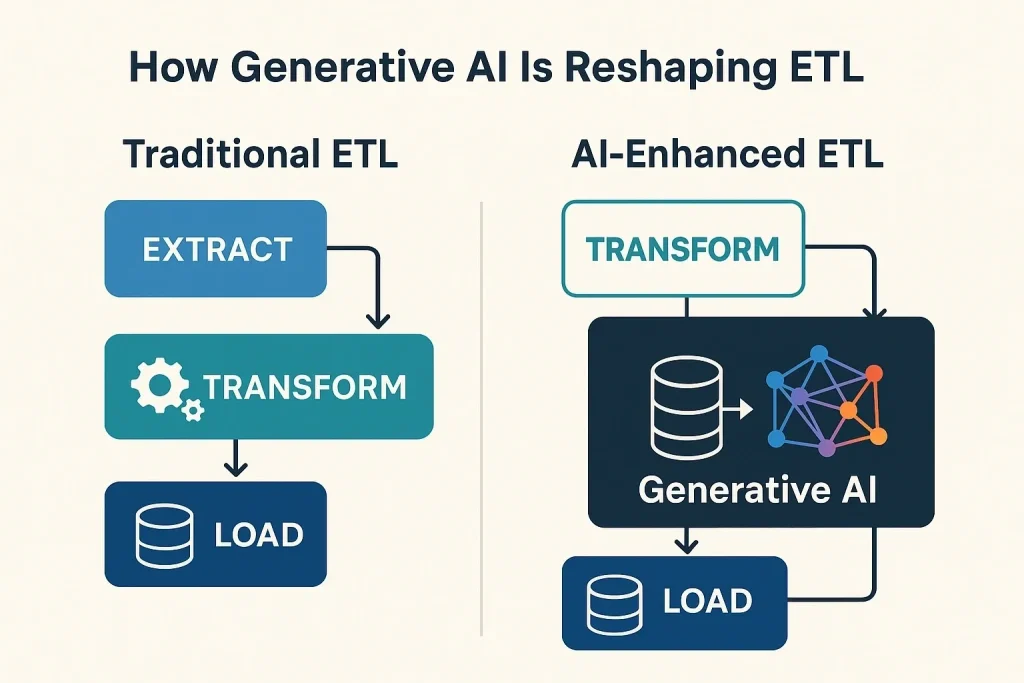
Data Transformation
3. Data Quality & Observability
- Predicts data quality incidents
- Suggests automated data tests
- Provides natural-language explanations for failing pipelines
- Recommends transformations to fix skew or missing values
Mini Data Quality Rules
ASSERT COUNT(*) WHERE amount < 0 = 0; ASSERT COUNT(DISTINCT customer_id) > 0;
In a retail pipeline, GenAI detected a sudden drop in daily order counts before dashboards refreshed. Instead of raising a generic alert, it explained that a late-arriving upstream file caused incomplete aggregates and recommended delaying downstream jobs.
Platforms like Monte Carlo, Accure AI, and Databricks Lakehouse AI now include GenAI copilots.
Data Observability
4. Data Modeling & Schema Design
You can describe your business scenario in plain English:
“We need a Sales Fact table linked with Customers, Products, and Regions.”
GenAI generates:
- ERDs
- Star schemas
- Naming conventions
- dbt model structure
- Best-practice modeling recommendations
Example: A logistics company used GenAI to auto-create Data Vault hubs and satellites from raw event streams—reducing modeling time from weeks to minutes.
5. Metadata Management & Data Catalogs
Modern catalogs allow users to:
- Ask natural-language questions like “Where does revenue come from?”
- Discover data assets across warehouses
- Generate column descriptions automatically
- Build lineage diagrams using SQL parsing and LLM reasoning
6. Automated Documentation
GenAI automatically generates:
- Pipeline documentation
- ERD explanations
- Column-level definitions
- Data quality rules
- Change logs
- Architecture diagrams
Tools include:
- Databricks AI Assistant
- dbt Docs AI
- ReadMe AI with LLMs
7. Intelligent Orchestration & Monitoring
GenAI enables self-healing pipelines by:
- Restarting failed tasks with modified parameters
- Explaining Airflow DAG failures in plain English
- Identifying resource bottlenecks
- Predicting SLA breaches
For example, when an Airflow task fails due to executor memory limits, the GenAI copilot summarizes the root cause and recommends configuration changes—saving hours of manual log analysis.
8. GenAI for Data Governance & Compliance
- Identify PII automatically
- Recommend masking and anonymization
- Classify data sensitivity
- Suggest RBAC policies
In banking platforms, GenAI introduces incremental AML feature computation and caching, reducing regulatory batch compute costs by ~35% while still meeting compliance SLAs.
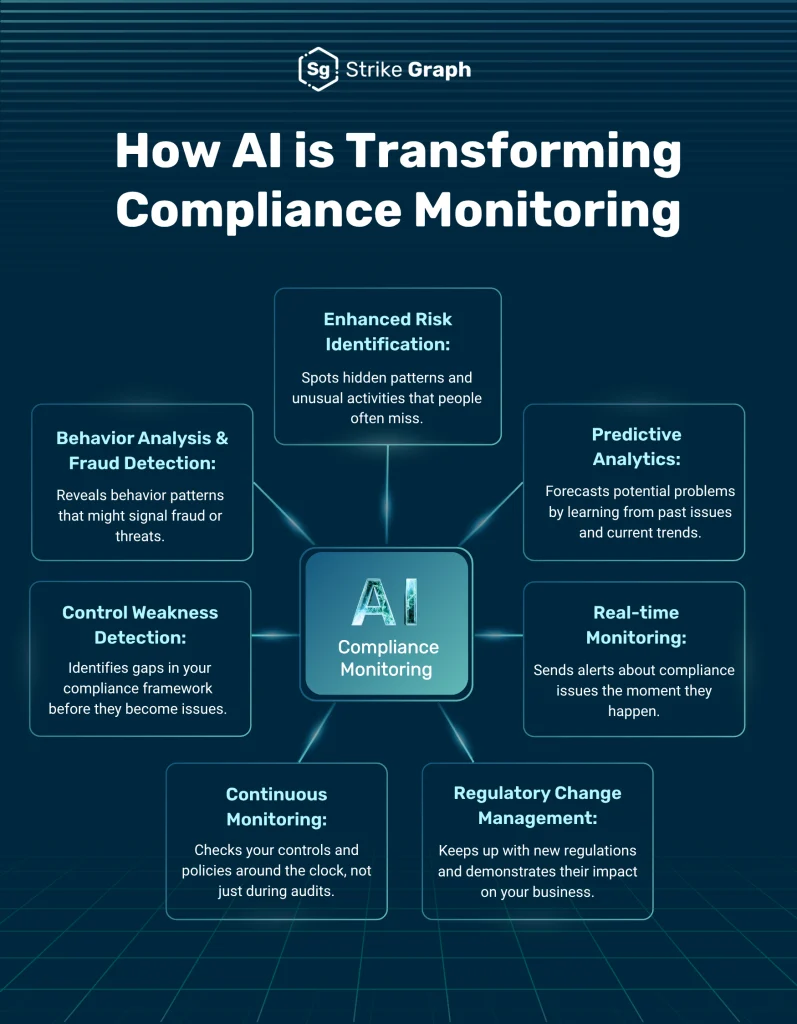
AI Compliance Monitoring
End-to-End Example: What an AI-Powered Data Pipeline Looks Like
Building a Customer 360 pipeline traditionally requires months of effort. With GenAI, it becomes automated and intelligent.
1. Business Requirement
Create a Customer 360 dashboard with customer profiles, behavioral metrics, and churn prediction. Refresh daily.
2. AI-Generated Ingestion Layer
- CRM (Salesforce)
- Transactional databases
- Website clickstream logs
- Support ticketing systems
Auto-Generated Ingestion Logic
ingest("salesforce", incremental=true)
ingest("transactions", cdc=true)
ingest("clickstream", streaming=true)
3. AI-Assisted Data Transformation
SELECT c.customer_id,
SUM(t.amount) AS lifetime_value,
COUNT(s.ticket_id) AS support_cases
FROM customers c
LEFT JOIN transactions t
LEFT JOIN support_tickets s
GROUP BY c.customer_id;
4. AI-Driven Data Modeling
- DimCustomer
- FactInteractions
- FactTransactions
- FactSupportTickets
5. Automated Data Quality & Observability
- Detects missing data
- Flags anomalies
- Creates validation rules automatically
6. Machine Learning for Churn Prediction
- Feature selection
- Model training
- Explainability
- Production scoring pipelines
Outcome
The entire pipeline is delivered in one-third of the time, fully documented, monitored, and optimized—reducing development effort by 60% and cloud costs by 30–50%.
Top GenAI Tools Transforming Data Engineering in 2024–2025
- Databricks Genie / AI Assistant: PySpark, SQL, DLT generation
- AWS Glue GenAI: ETL generation, schema drift handling
- Snowflake Cortex AI: NL SQL, governance
- dbt AI: Models and documentation
- Atlan / Alation / Collibra: Metadata intelligence
- Airflow Copilot: DAG generation, failure explanation
Challenges & Considerations
- Hallucinations – always review generated output
- Data privacy and masking
- Strong guardrails
- Skill shift toward prompt engineering
Where GenAI Should Be Used Carefully (or Avoided)
- Mission-critical transformations without human review
- Regulatory logic where determinism is mandatory
- Security-sensitive pipelines without strict guardrails
- High-frequency trading or real-time risk scoring systems
In practice, GenAI should act as an accelerator and advisor—not an autonomous decision-maker for irreversible business logic. Mature teams treat GenAI output as “code suggestions,” not production truth.
What the Future Looks Like
- Autonomous pipelines
- AI-first ETL
- Natural language interfaces
- AI-enhanced data mesh
- Continuous optimization agents
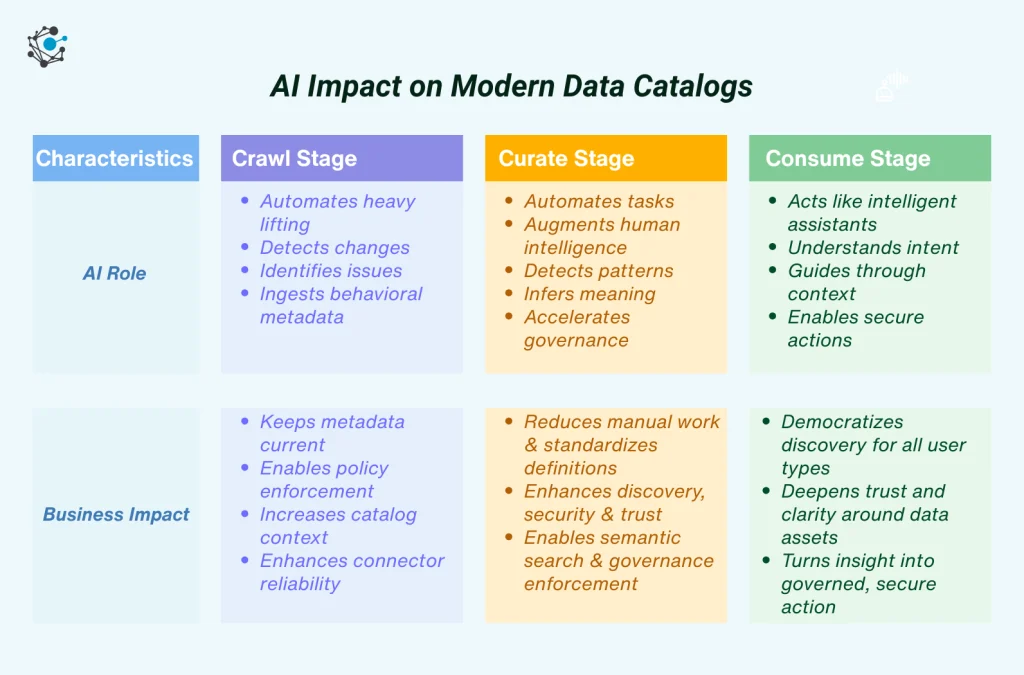
AI Impact on Modern Data Catalogs
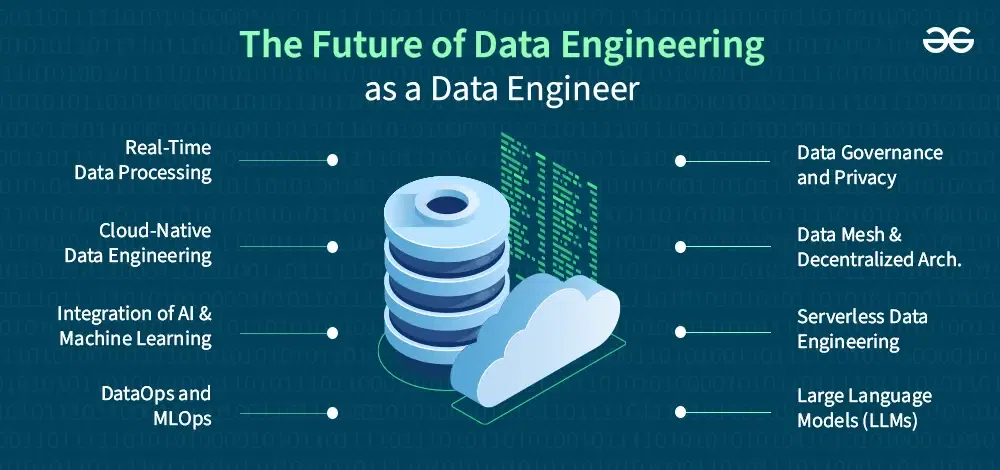
Future of Data Engineering
Before vs After: Measured Impact
| Metric | Before GenAI | After GenAI |
|---|---|---|
| Pipeline Development Time | 6–8 weeks | 2–3 weeks |
| Production Failures | Frequent | Reduced by ~40% |
| Cloud Cost | Baseline | 30–50% optimized |
Conclusion
GenAI is not replacing data engineers—it is elevating them.
- 40–70% faster development
- 30–50% cost optimization
- Higher reliability
- Improved documentation and governance
GenAI is not just an upgrade—it’s a transformation of how data engineering is practiced.

