Implementing configurable SMART on FHIR authentication with Node.js
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of health-tech, interoperability and security are critical. SMART on FHIR (Substitutable Medical Applications, Reusable Technologies on Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) has emerged as a robust standard to create apps that integrate seamlessly with Electronic Health Record systems.
This blog, which is meant for developers building healthcare apps, covered the full lifecycle of implementing a configurable SMART on FHIR authentication system using Node.js and Express, with support for both Epic and Cerner EHR.
What is FHIR?
FHIR (pronounced as fire) is a standard developed by HL7 to simplify the exchange of healthcare data between different systems and applications
Key features:
- Breaks healthcare data into small, modular components called resources (e.g Patient, Encounter)
- Defines standard structure, content, and semantics for these.
- Exposes healthcare resources via RESTful APIs.
Example of simple Patient resource:
{
"resourceType": "Patient",
"id": "example",
"name": [{"family": "Sheikh", "given": ["Mavin"]}],
"gender": "male",
"birthDate": "1980-26-26"
}
What is SMART on FHIR?
SMART on FHIR is an open standard that allows third-party apps to connect with healthcare systems using FHIR Rest API’s and standardised OAuth 2.0 authorization flows.
SMART App Launch Types
SMART on FHIR defines three ways to launch the app:
- Standalone Launch: Launched directly by the user outside the EHR.
- EHR (also called as Embedded) Launch: Launched within an EHR application.
- Backend systems: For Apps without direct end user or patient interaction (In this blog we will only discuss first two launch types)
Standalone Launch Sequence
- Register the App with the FHIR server to get a Client ID (e.g, via Epic or Cerner).
- The user visits your app directly outside of EHR.
- Get SMART well known configuration from the FHIR server (also called as conformance statement).
- Redirect user to the FHIR server’s authorize endpoint.
- FHIR server authenticates user and redirects to your callback url with an authorization code.
- Exchange the code at the token endpoint to get access token.
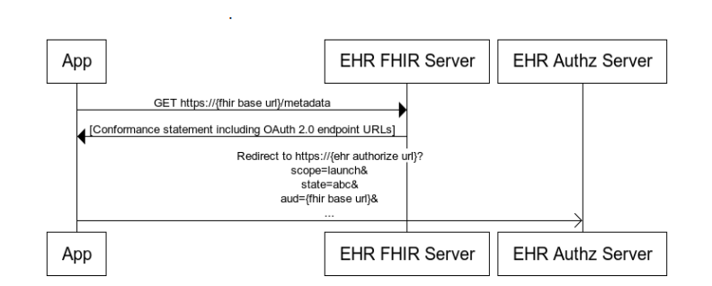
Standalone launch sequence
EHR (Embedded) Launch Sequence
EHR (Embedded) Launch Sequence is same as standalone, except:
- App is launched from within the EHR.
- EHR passes a launch context and iss (FHIR base URL).
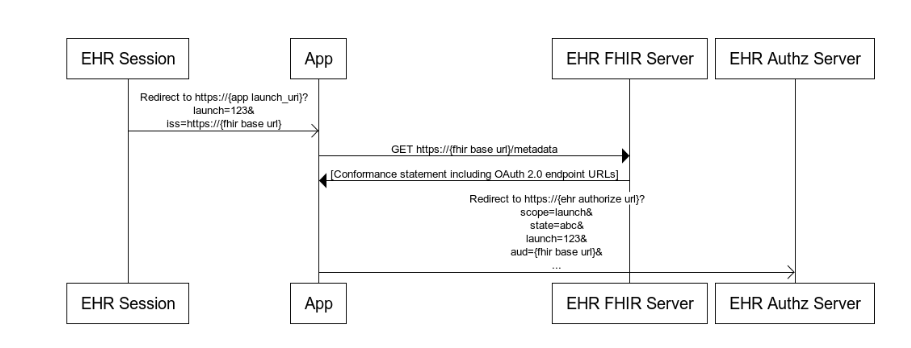
Embedded launch sequence
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Register Your App
Register your app with the desired FHIR platform (Epic, Cerner etc) to get client credentials and configure redirect URI.
Step 2: Setup Express App (app.ts)
import express, { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
import authRoutes from './routes/auth';
import { appConfig } from './config';
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.use('/auth', authRoutes);
app.listen(appConfig.port, () => {
console.log(`Auth Server running at ${appConfig.origin}`);
});
Step 3: Define Routes (routes/auth.ts)
import express from 'express';
import {
standaloneLaunch,
standaloneLaunchCallback,
embeddedLaunch,
embeddedLaunchCallback,
} from '../controllers/auth';
const router = express.Router();
router.get('/standalone/:provider', standaloneLaunch);
router.get('/callback', standaloneLaunchCallback);
router.get('/embedded', embeddedLaunch);
router.get('/embeddedCallback', embeddedLaunchCallback);
export default router;
Step 4: Add Configuration File in root folder (config.ts)
import { EhrProvider } from './enums/ehrProvider'
import { EhRAuthConfig, AppConfig } from './types';
require('dotenv').config();
export const appConfig: AppConfig = {
port: process.env.PORT! || '3000',
host: process.env.HOST!,
origin: `${process.env.HOST}:${process.env.PORT}`,
}
export const ehrAuthConfig: Record<EhrProvider, EhRAuthConfig> = {
[EhrProvider.EPIC]: {
authorizationUrl: process.env.EPIC_AUTH_URL!,
tokenUrl: process.env.EPIC_TOKEN_URL!,
clientId: process.env.EPIC_CLIENT_ID!,
standaloneRedirectUrl: appConfig.origin + '/auth/callback',
embeddedRedirectUrl: appConfig.origin + '/auth/embeddedCallback',
fhirApiBase: process.env.EPIC_FHIR_API_BASE!,
scope: 'openid profile user/Patient.read patient/MedicationRequest.write'
},
[EhrProvider.CERNER]: {
authorizationUrl: process.env.CERNER_AUTH_URL!,
tokenUrl: process.env.CERNER_TOKEN_URL!,
clientId: process.env.CERNER_CLIENT_ID!,
standaloneRedirectUrl: appConfig.origin + '/auth/callback',
embeddedRedirectUrl: appConfig.origin + '/auth/embeddedCallback',
fhirApiBase: process.env.CERNER_FHIR_API_BASE!,
scope: 'openid profile user/Patient.read'
}
}
Step 5: Environment Variables (.env)
# App PORT=3000 HOST=http://localhost # EPIC AUTH CONFIG EPIC_AUTH_URL=https://fhir.epic.com/interconnect-fhir-oauth/oauth2/authorize EPIC_TOKEN_URL=https://fhir.epic.com/interconnect-fhir-oauth/oauth2/token EPIC_CLIENT_ID=<your-client-id> EPIC_FHIR_API_BASE=https://fhir.epic.com/interconnect-fhir-oauth/api/FHIR/R4 # CERNER AUTH CONFIG CERNER_AUTH_URL=https://authorization.cerner.com/tenants/ec2458f2-1e24-41c8-b71b-0e701af7583d/protocols/oauth2/profiles/smart-v1/personas/provider/authorize CERNER_TOKEN_URL=https://authorization.cerner.com/tenants/ec2458f2-1e24-41c8-b71b-0e701af7583d/protocols/oauth2/profiles/smart-v1/token CERNER_CLIENT_ID=<your-client-id> CERNER_FHIR_API_BASE=https://fhir-ehr-code.cerner.com/r4/ec2458f2-1e24-41c8-b71b-0e701af7583d
Step 4: Add Controllers (controllers/auth.ts)
import { Request, Response } from 'express';
import { ehrAuthConfig } from '../config';
import { EhrProvider, HttpStatusCode, HttpMethod } from '../enums';
import { getWellKnownSmartConfiguration } from '../services/fhir.service';
export const standaloneLaunch = (req: Request, res: Response): void => {
const provider = req.params.provider as EhrProvider;
if (!provider) {
console.log('Missing emr param')
res.status(HttpStatusCode.BAD_REQUEST).send('Missing emr param');
return
}
const authConfig = ehrAuthConfig[provider]
try {
const authParams = new URLSearchParams({
response_type: "code",
client_id: authConfig.clientId,
redirect_uri: authConfig.standaloneRedirectUrl,
scope: authConfig.scope,
aud: authConfig.fhirApiBase,
state: provider,
});
const redirectUrl = `${authConfig.authorizationUrl}?${authParams.toString()}`;
res.redirect(redirectUrl);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', (error as Error).message);
res.status(HttpStatusCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).send('Internal server error');
}
};
export const standaloneLaunchCallback = async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<void> => {
const { code, state } = req.query;
const authConfig = ehrAuthConfig[state as EhrProvider]
try {
const params = new URLSearchParams({
grant_type: 'authorization_code',
code,
redirect_uri: authConfig.standaloneRedirectUrl,
client_id: authConfig.clientId,
});
// Exchanges Auth Code for an Access Token
const response = await fetch(authConfig.tokenUrl, {
method: HttpMethod.POST,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
},
body: params.toString(),
});
if (!response.ok) {
const errorData = await response.text();
console.error('Token exchange failed:', errorData);
res.status(HttpStatusCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).send('Token exchange failed');
return;
}
const data = await response.json()
const { access_token, token_type, id_token, scope } = data;
res.json({ access_token, token_type, id_token, scope });
} catch (error) {
res.status(HttpStatusCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).send('Internal server error');
}
}
function getEhrProviderByIssuer(fhirApiBase: string): EhrProvider {
return Object.entries(ehrAuthConfig).find(
([, config]) => config.fhirApiBase === fhirApiBase
)?.[0] as EhrProvider;
}
let tokenUrl: string
export const embeddedLaunch = async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<any> => {
const fhirServerUrl: any = req.query.iss!;
const launchContext: any = req.query.launch!;
const ehrProvider = getEhrProviderByIssuer(fhirServerUrl)
const authConfig = ehrAuthConfig[ehrProvider]
if (!fhirServerUrl || !launchContext) {
console.log('Missing iss or launch parameter')
return res.status(HttpStatusCode.BAD_REQUEST).send('Missing iss or launch parameter.');
}
try {
const smartConfig = await getWellKnownSmartConfiguration(fhirServerUrl)
const authorizeUrl = smartConfig.authorization_endpoint;
tokenUrl = smartConfig.token_endpoint;
const authParams = new URLSearchParams({
response_type: "code",
client_id: authConfig.clientId,
redirect_uri: authConfig.embeddedRedirectUrl,
scope: "launch patient/*.read",
launch: launchContext.toString(),
aud: fhirServerUrl.toString(),
state: ehrProvider
}
const redirectUrl = `${authorizeUrl}?${authParams.toString()}`;
res.redirect(redirectUrl);
} catch (error) {
res.status(HttpStatusCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).send("Failed to launch");
}
}
export const embeddedLaunchCallback = async (req: Request, res: Response): Promise<any> => {
const { code, state } = req.query;
const authConfig = ehrAuthConfig[state as EhrProvider]
try {
const tokenParams = new URLSearchParams({
grant_type: 'authorization_code',
code: code as string,
client_id: authConfig.clientId,
redirect_uri: authConfig.embeddedRedirectUrl,
});
const tokenResponse = await fetch(tokenUrl, {
method: HttpMethod.POST,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
}
body: tokenParams.toString(),
});
if (!tokenResponse.ok) {
const errorText = await tokenResponse.text();
return res.status(HttpStatusCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).send('Error exchanging code for token');
}
const tokenData = await tokenResponse.json();
const accessToken = tokenData.access_token as string;
res.send(`Access token received! ${accessToken}`);
} catch (err) {
res.status(HttpStatusCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).send('Unexpected error during token exchange');
}
}
module.exports = {
standaloneLaunch,
standaloneLaunchCallback,
embeddedLaunch,
embeddedLaunchCallback,
};
Note: In standalone launch, EHR provider’s name (e.g Epic or Cerner) is passed in state parameter. This allows the callback handler to determine which config to use when exchanging auth code for a token.
Testing Your Application
Standalone Launch
Start your server: npm run start and try:
Epic: http://localhost:3000/auth/standalone/epic
Cerner: http://localhost:3000/auth/standalone/cerner
You will be redirected to the EHR login screen. After successfully logging in, you will receive access token.
Embedded Launch
To simulate embedded launch use the SMART App Launcher with your embedded endpoint: http://localhost:3000/auth/embedded
Using token to access FHIR resources
Once you receive valid access token, your can now access protected patient data from the EHR database using FHIR Rest APIs. You need to pass access token in authorization header as a Bearer token.
GET <fhir-server-url>/Patient/{id}
Authorization: Bearer Nxfve4q3H9TKs5F5vf6kRYAZqz...
Adding Support for a New EHR
Adding support for another SMART on FHIR compliant EHR is simple, Just add another provider entry in ehrAuthConfig inside config.ts. No additional logic required!

