Redis Cluster backups and restoration
Redis Cluster backups to Amazon S3 using a single bash script and cron. It’s safe, slot-aware (backs up every node you run it on), and waits for BGSAVE to finish before uploading.
What this setup does
- Runs on each Redis node, including masters and replicas, so you get a full cluster backup.
- It triggers BGSAVE, waits for the snapshot to finish, and then uploads your persistence files to S3:
- dump.rdb
- appendonly.aof (if AOF or RDB+AOF is enabled)
- It encrypts the data at rest in S3 using SSE-S3 or SSE-KMS. It also adds retention by using an S3 lifecycle rule and performs basic integrity checks.
Prerequisites (once per node)
- Install tools
apt-get update && apt-get install -y awscli jq
# or: yum install -y awscli jq - AWS credentials on the node
Prefer an EC2 instance profile role; otherwise configure aws configure. - IAM policy for the instance role
Grant Put/Get/List to your chosen bucket, plus (optional) KMS encrypt: - Decide where Redis stores data
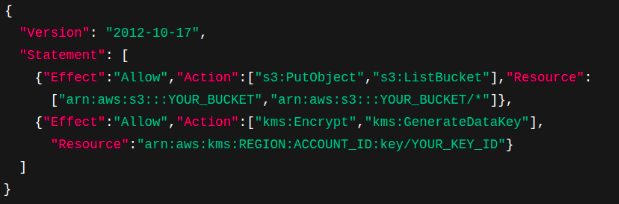
Policy
Check redis.conf:
1. dir /var/lib/redis
2. dbfilename dump.rdb
3. appendonly yes|no and appendfilename appendonly.aof - S3 bucket & (optional) lifecycle
Create the bucket s3://your-redis-backups/ and add a lifecycle rule. For example, keep the data for 30 days, then move it to Glacier or delete it.
2) Drop-in backup script
Save as /usr/local/bin/redis-cluster-backup.sh and make it executable.
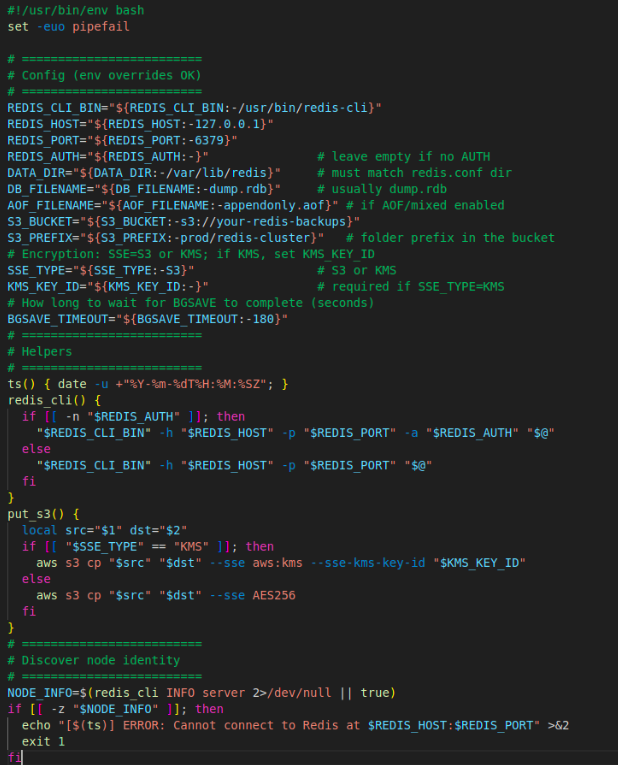
Script page -1
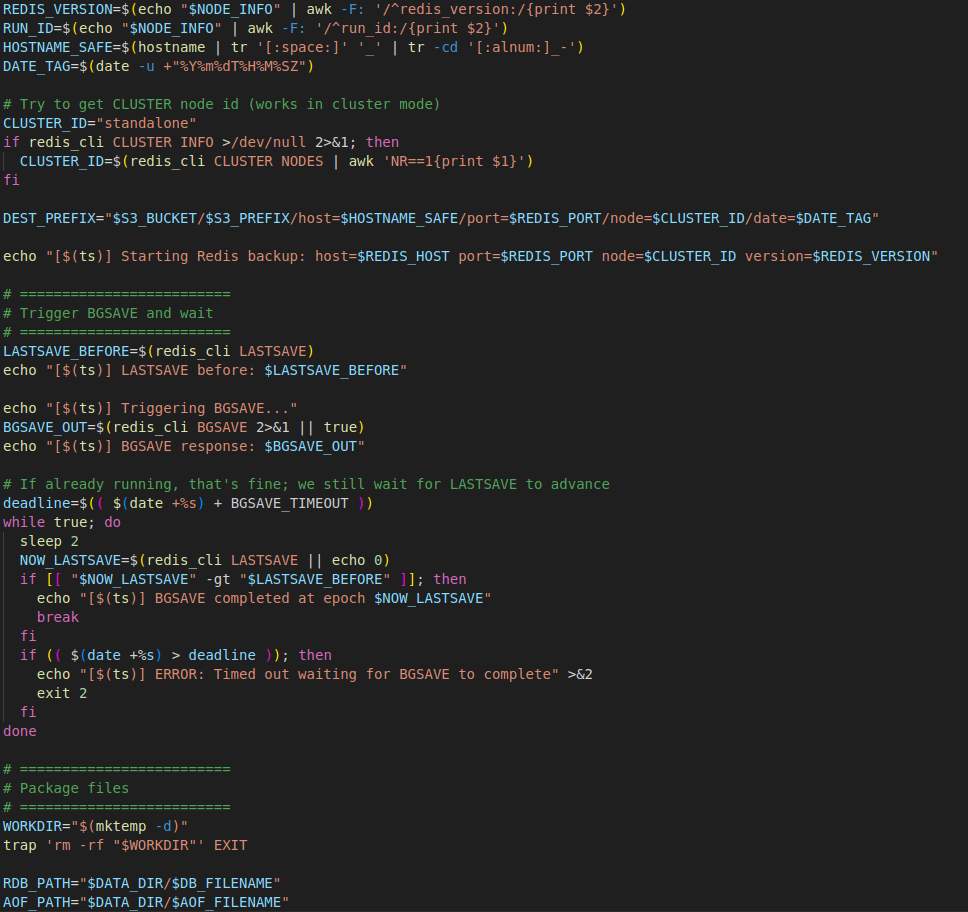
Script page – 2
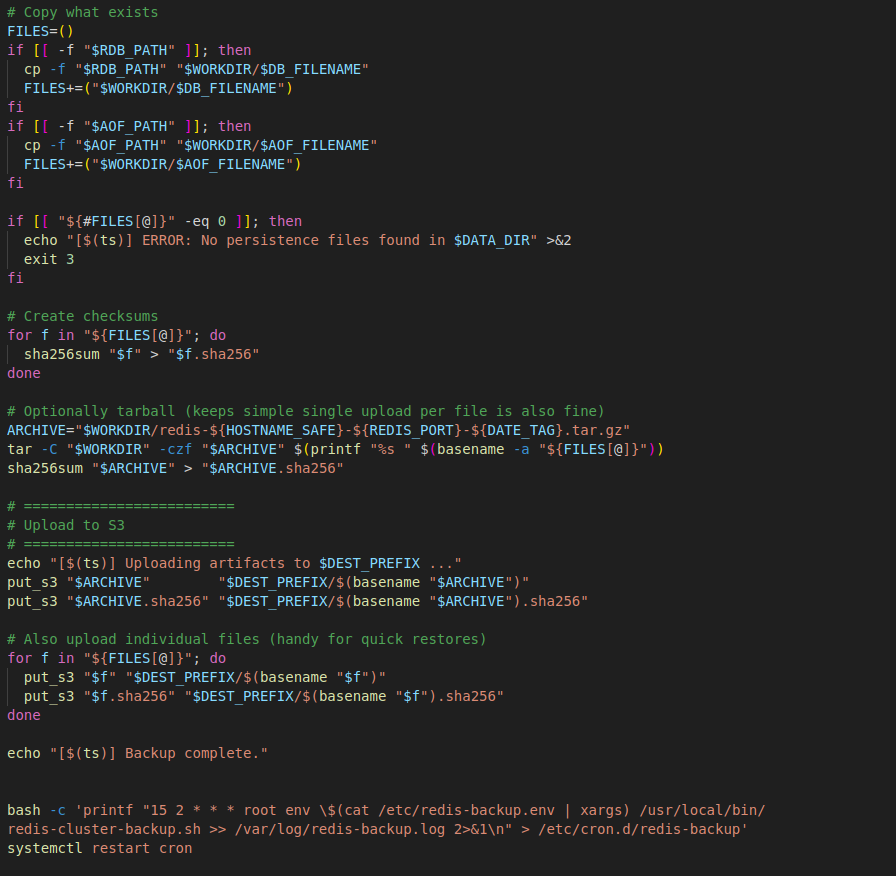
Script page – 3
Optional: a small env file for easy overrides:-
Create /etc/redis-backup.env (owned & readable by root only):
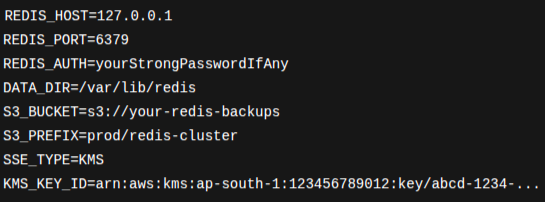
env file
Then call the script with:
Cmd
3) Scheduling with Cron
Run daily at 02:15 local time or at any specific time as per your need:

Cron
5) Restore (node or cluster)
Standalone or single node (lab/staging)
- Stop Redis.
- Replace files in dir with your backup:
- If restoring RDB(Redis Database File): put the dump.rdb(point-in-time snapshot).
- If AOF(Append Only File) or mixed: put appendonly.aof (and ensure appendonly yes).
- Start Redis — it loads whichever persistence you’ve enabled.
Cluster restore (same topology)
- Restore each node from its own backup (masters & replicas).
- Start nodes; verify with:

Redis
- Ensure slot ownership and replication match your desired layout.(If you are re-creating a cluster from scratch, use cluster create with the master/replica mapping and then restore files before opening to traffic.)

