What is Serverless and How JavaScript Fits Into It
Introduction
Serverless. A term that often confuses at first glance. Because servers are still there. You just don’t touch them. You don’t set them up, scale them, or patch them. That’s someone else’s job now — the cloud provider’s.
And the most common example of this approach is AWS Lambda.
For many developers, Lambda is where “serverless” stops being a buzzword and starts feeling real. In this blog, we’ll explore what serverless means, how Lambda works, and why JavaScript fits perfectly into this model.
What is Serverless AWS Lambda, Really?
Let me put it simply.
- You write small functions.
- Something happens (an event).
- Your function runs.
- Cloud does the rest – scaling, availability, billing.
- You focus on the logic. The “infrastructure magic” stays invisible.
Best analogy I’ve found – Ordering food. You don’t run the kitchen, you don’t hire the chef. You just order, and it arrives. Serverless is the same. Write function. Done.
Why JavaScript Fits Right In
Here’s where JavaScript comes in. AWS Lambda supports multiple languages, but Node.js has become one of the most popular choices. Why?
Familiarity → Most developers already know JavaScript.
Event-driven → Lambda itself is event-driven, just like Node.js.
Speed → Cold starts are faster compared to heavier runtimes.
Why Developers Choose Serverless (and Lambda)
- Developers love serverless not because it’s fancy, but because it solves painful problems of traditional servers. Some highlights:
- Effortless scaling – With EC2 (traditional servers), you’d worry about traffic spikes and provisioning instances. Lambda handles it automatically.
- Pay only for what you use – In Lambda, you pay for execution time (measured in milliseconds), not idle hours. No wasted cost like keeping servers running 24/7.
- No babysitting servers – You write your code, Lambda runs it. No patching, no monitoring uptime, no OS updates.
- Fast experiments – Want to test an idea? Deploy it in minutes without worrying about infrastructure.
For many developers, this is a game-changer.
Real-World Scenarios Where Lambda Wins
Let’s step outside theory. Where does Lambda actually make sense?
- Image Processing on the Fly
Upload an image to S3, trigger a Lambda to resize/convert it instantly. No need for a dedicated image-processing server. - Serverless APIs
Use API Gateway + Lambda to create REST APIs. Scales from 10 requests/day to millions/month without changing a thing. - Event-Driven Automation
Example: a file lands in S3 → Lambda cleans, validates, or transforms it → sends file’s data to a database. - IoT & Streaming Data
Devices send events; Lambda processes them in real time, pushing clean data into DynamoDB or analytics pipelines.
How Lambda Fits in the Flow
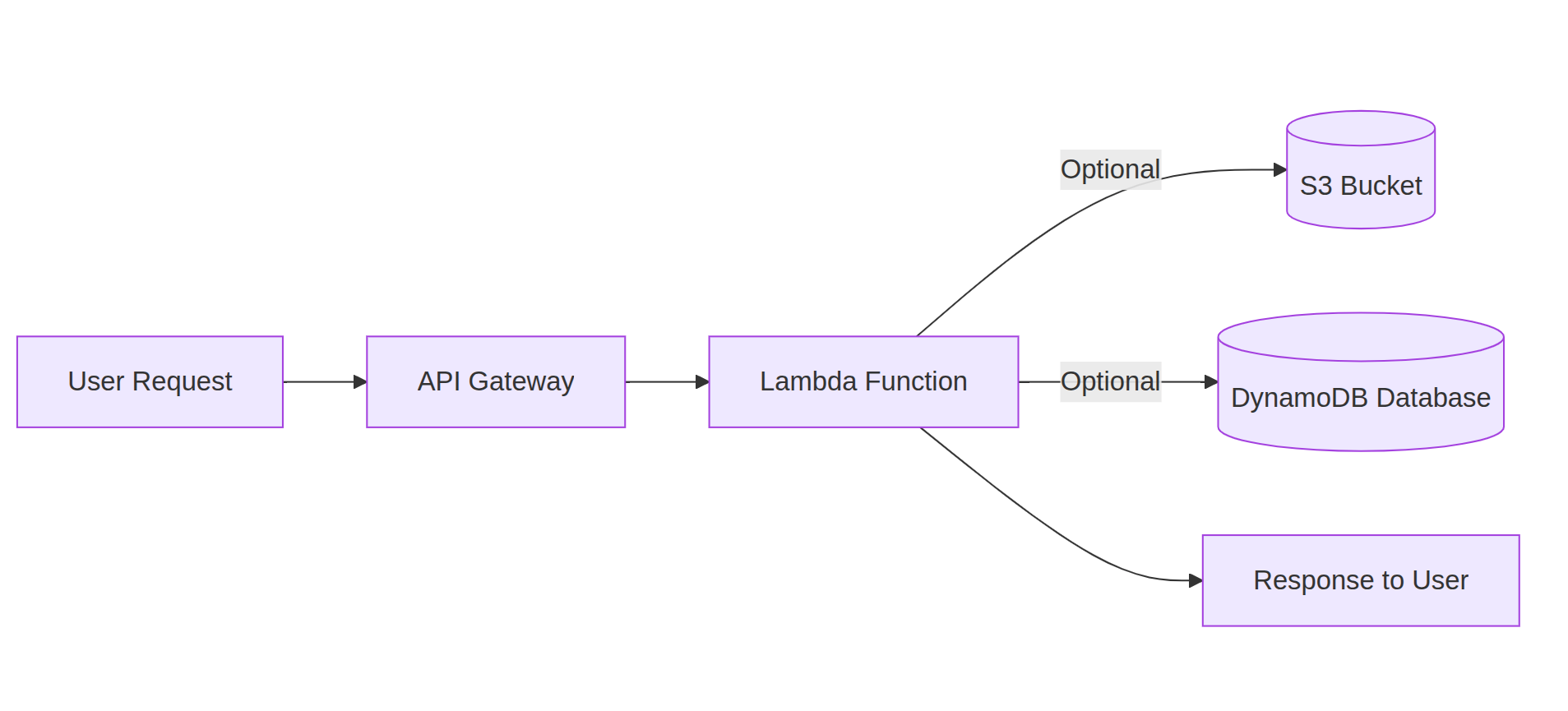
Lambda Mermaid Diagram
In simple words:
- A user sends a request (say from a web app).
- API Gateway receives it and forwards it to Lambda.
- Lambda runs your JavaScript code.
- If needed, Lambda stores/retrieves data from S3 or DynamoDB.
- Finally, Lambda sends the response back to the user.
- That’s it. Serverless in action.
What’s New in Lambda?
Serverless isn’t standing still. AWS keeps adding improvements that make Lambda more powerful and easier to use:
- Faster cold starts → Functions start quicker, so user-facing apps feel more responsive.
- Container image support → You can now package Lambda code as Docker images if you prefer.
- Graviton2 processors → ARM-based Lambdas that give better performance at lower cost.
These updates mean serverless is no longer just for small applications , it is ready for bigger workloads too.
Example: A Simple API with Lambda
Let’s imagine we want a basic API that says hello. In a traditional setup, we’d spin up an Express server, deploy it on EC2, manage scaling.
With Lambda, it’s simpler.
Make a Lambda Function
- In AWS Console → Lambda → Create function.
- Pick Author from scratch.
- Choose Node.js runtime.
- Name it. Create it. Done.
Write a function in Node.js:
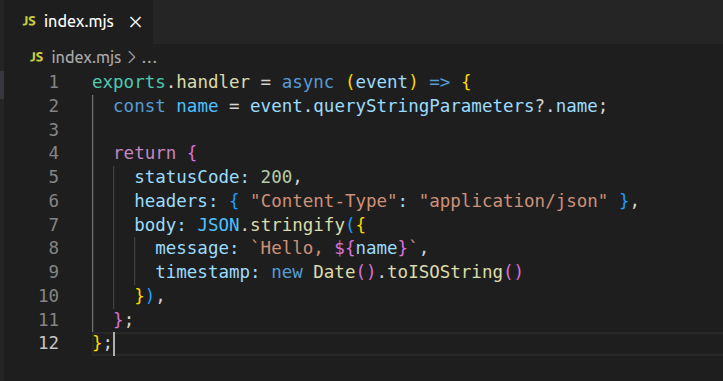
Lambda handler
Attach With API Gateway
- Go to API Gateway → Create API.
- Choose HTTP API.
- Add a route: GET /hello
- Point it to your Lambda.
- Deploy.
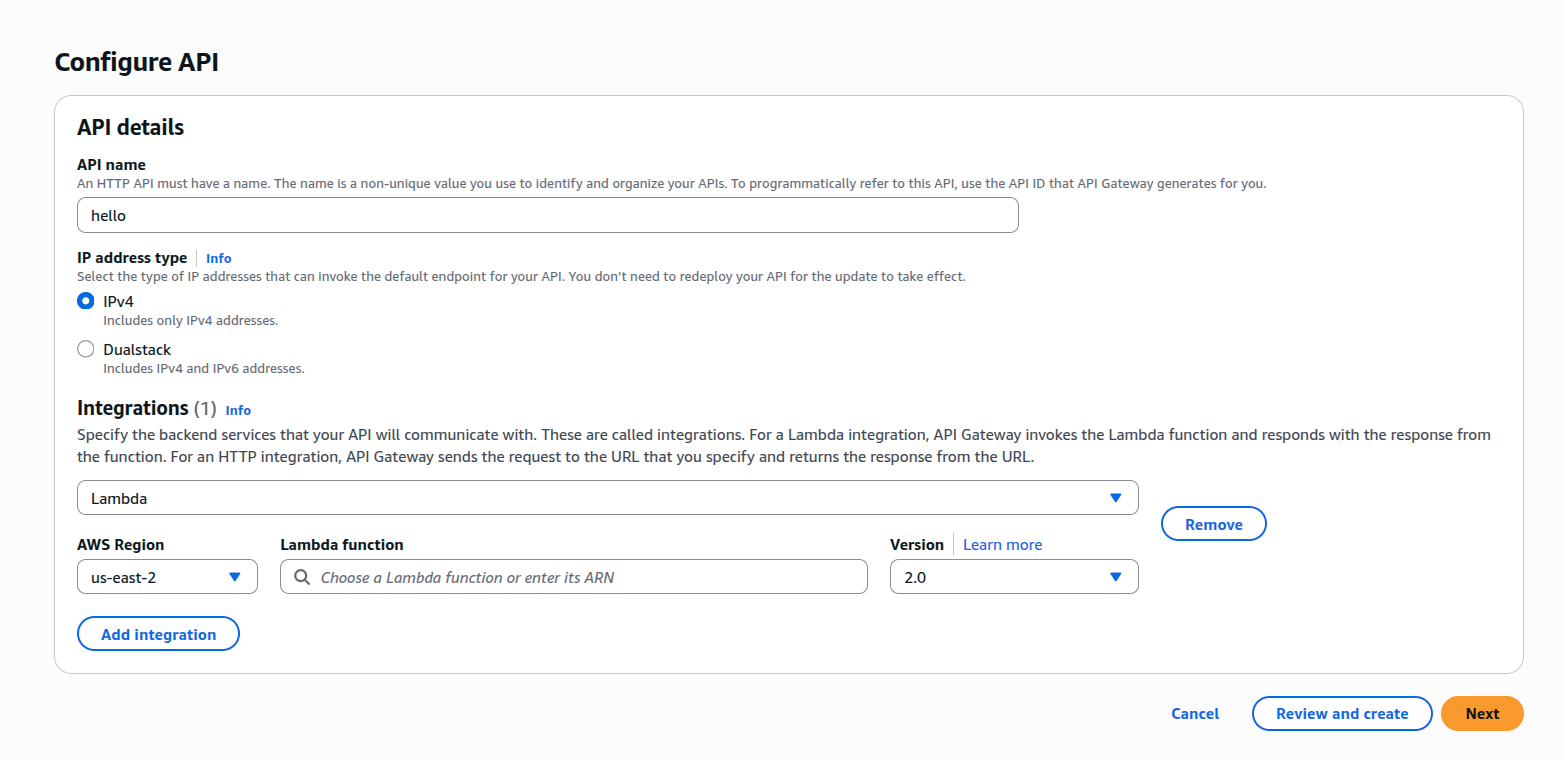
AWS Api Gateway
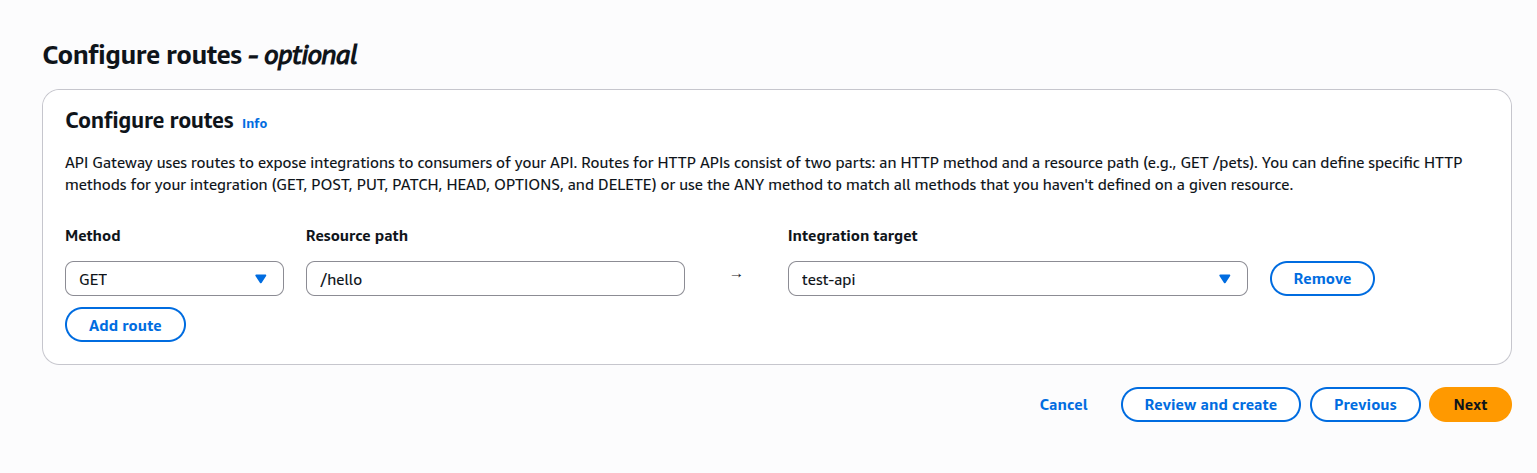
Api gateway add route
To Test: Hit the AWS API Gateway URL
curl “https://<your-api-gw-id>.execute-api.<aws-region>.amazonaws.com/hello?name=<your-name>”
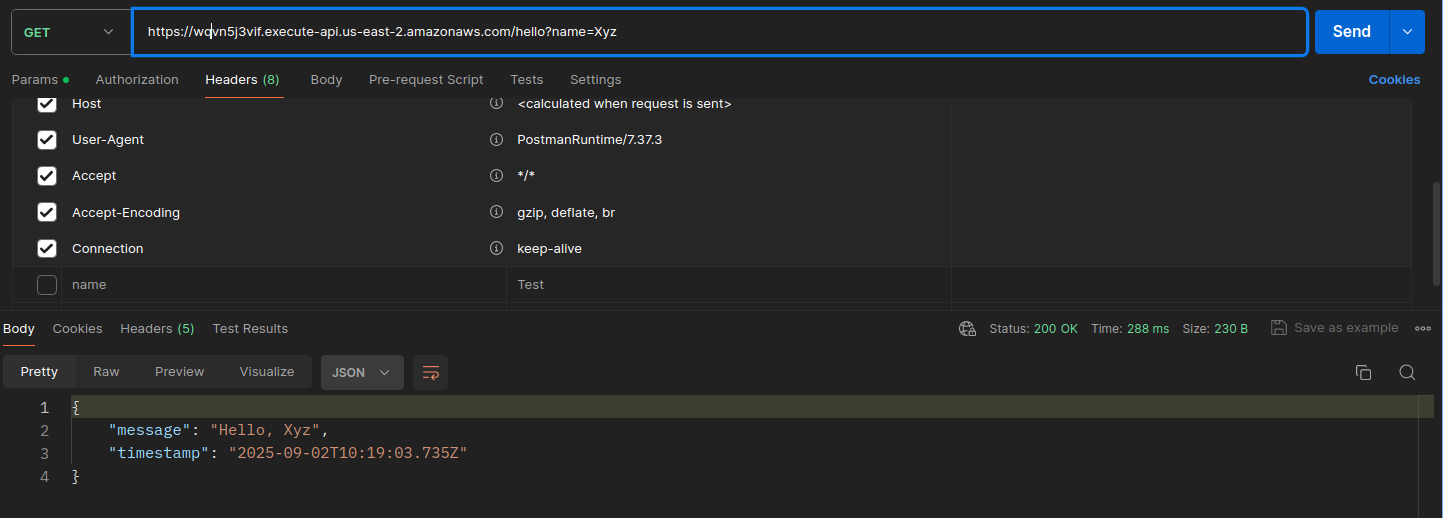
postman api response
Conclusion
Serverless isn’t magic. But sometimes, it feels like it.
You write the logic. The cloud takes care of everything else.
Combine that with JavaScript , a language you probably already use daily and you’ve got something powerful:
APIs that scale without effort.
Costs that match usage.
And freedom from server babysitting.
So, next time you’re spinning up an Express server on an EC2 instance for a small API, pause for a second. Think :
“Can this just be a Lambda?” yes , It can.

