OTT Ad Insertion Technologies: SSAI, CSAI, and the Future of OTT Advertising with AI
The OTT streaming industry has grown rapidly over the past decade and has redefined how the end user consumes content. This growth has also driven demand for sophisticated OTT app development solutions that can support advanced advertising technologies like SSAI and CSAI, ensuring seamless monetization and scalable performance. With the worldwide shift from linear television to digital streaming, advertising remains a critical monetisation model across various platforms.
To effectively serve the ads along with a seamless content viewing experience, the OTT ecosystem relies on two primary methods
- Server Side Ad Intention (SSAI)
- Client Side Ad Insertion (CSAI).
Both methods have their own advantages, technical complexities, and business implications.
With the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI), these methods are evolving and enabling personalised and predictive ad experiences.
Understanding the Ads Insertion: CSAI vs SSAI
Client Side Ad Insertion (CSAI)
CSAI is the conventional method of delivering ads. In this method, the video player executes the request and then fetches and renders the ads during the content playback; an important consideration for OTT platform development, particularly for mobile and web apps where SDK integrations and ad rendering impact user experience.
How CSAI Works:
Client-Side Ad Insertion (CSAI) is entirely executed in the user’s device by the video player. The player controls when to request ads, how to render them, and what events to track.
- Playback Initialization
- User taps “Play” on the OTT app.
- The player fetches the master manifest (HLS or DASH) and begins buffering the main content.
- The app/player loads the relevant ad SDK (IMA SDK, GAM, FreeWheel, or custom).
- Cue Point Detection
- The content manifest includes ad markers or metadata like: SCTE-35 markers
- The player monitors these markers during playback.
- Triggering an Ad Request
- When the player reaches an ad break:
- It pauses or stops content playback at the marker.
- The player constructs an ad request with parameters such as:
- user/device info
- content ID
- ad position (pre/mid/post-roll)
- app version
- geolocation
- device type
- The request is sent to the ad server using the protocols:
- VAST 4.x (standard XML-based response)
- VMAP (for multiple ad breaks)
- VPAID (for interactive ads)
- When the player reaches an ad break:
- Ad Server Decisioning
- The ad server returns:
- ad creative URLs (MP4, WebM)
- tracking events (start, quartiles, complete)
- click-through URLs
- companion ads
- ad sequencing (pod delivery)
- The ad server returns:
- Player Downloads the Ad Creative
- The player interrupts the main content stream.
- It separately fetches the ad’s media file from the CDN.
- Player buffers ad content → potential buffering if bandwidth is unstable.
- Ad Rendering in the Player
- The player:
- switches rendering context from content to ad
- plays the ad using the same or a secondary video element
- listens to quartile events
- The player:
- Tracking and Analytics
- During ad playback, the player fires:
- impression beacon
- start / 25% / 50% / 75% / complete
- error codes
- click events (if user taps an ad)
- These events are sent to: ad server
- During ad playback, the player fires:
- Resuming the Main Content
- When all ads in the pod finish:
- The player switches back to the main content stream
- Playback resumes from the exact timestamp where it stopped
- When all ads in the pod finish:
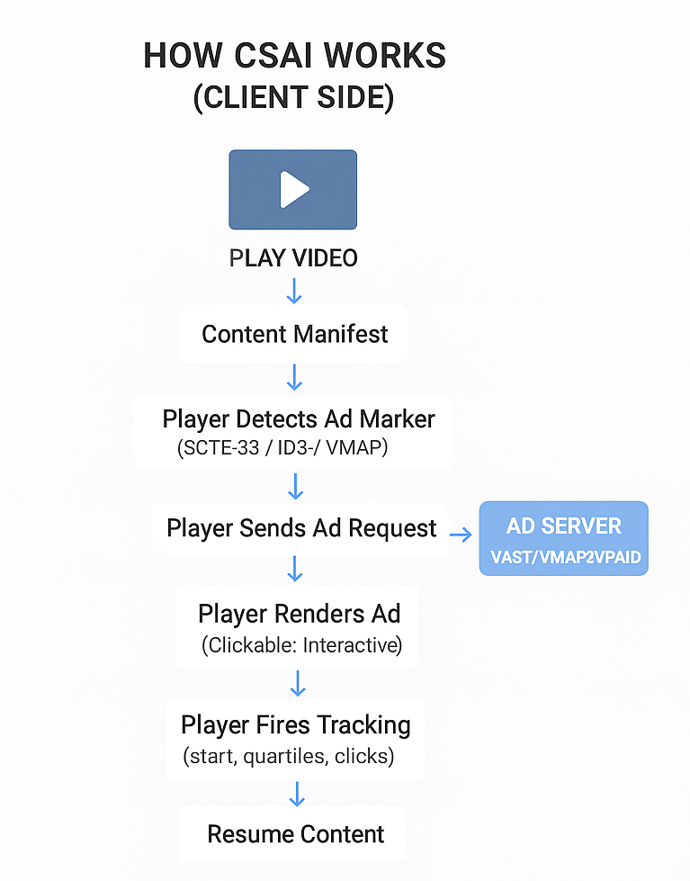
CSAI
Advantages of CSAI:
- Deep Insights: Offers real-time insights into impressions and interactions.
- Interactive: supports clickable and gamified ads.
- Targeting: Offers personalised ads based on the user behaviour.
Challenges of CSAI:
- Interrupted Playback: Switching between content and ad stream can cause buffering/ latency during playback.
- Ad Blockers: Ad requests can be blocked if the user’s device has an ad blocker.
- Device Support: Requires SDK integration across multiple devices and platforms.
Server Side Ad Insertion (SSAI)
Server-Side Ad Insertion (SSAI) moves most of the work away from the player to the backend, an architectural choice that many advanced OTT app development projects adopt to enhance playback smoothness and reduce client-side complexity. The player simply plays a single continuous stream with no switching between content and ad media.
- Playback Request from Client
- User clicks “Play”.
- The player requests the content manifest from the CDN / origin.
- Instead of hitting the origin directly, the request is routed through an SSAI stitching service (AWS MediaTailor, Google DAI, Brightcove, Yospace, etc.).
- SSAI Service Intercepts the Manifest Request
- The SSAI backend reads the manifest and identifies:
- ad break opportunities
- SCTE-35 markers
- VMAP definition (if present)
- content segments
- It then prepares for ad decisioning.
- The SSAI backend reads the manifest and identifies:
- Ad Server Request (Server-to-Server Call)
- SSAI now makes an S2S call to the ad server, including:
- IP address
- user agent
- content metadata
- positional metadata (pre-roll/mid-roll/post-roll)
- device category
- app/platform details
- session ID
- This call generally follows VAST 4.2 or VMAP standards.
- SSAI now makes an S2S call to the ad server, including:
- Ad Decisioning Returned from Ad Server
- The ad server responds with:
- list of ads
- creative URLs (MP4/TS)
- tracking URLs (impressions, quartiles)
- durations
- podding details (e.g., 2 ads back-to-back)
- Unlike CSAI, these creatives must be transcode-ready.
- The ad server responds with:
- Ad Transcoding & Normalization
- To ensure a seamless stream, the SSAI system transcodes the ads to match the content’s technical parameters:
- codec (H.264/H.265)
- resolution (e.g., 720p)
- bitrate ladder (multi-bitrate profiles)
- segment duration (common: 2s, 4s, 6s segments)
- This creates a uniform stream where ads and content are visually identical in structure.
- To ensure a seamless stream, the SSAI system transcodes the ads to match the content’s technical parameters:
- Ad Stitching
- The SSAI service now:
- converts transcoded ads into segmented media
- inserts these segments into the content manifest
- updates sequence numbers and timeline continuity
- ensures no discontinuities or timestamp jumps
- The output is a single HLS/DASH manifest containing both
- content segments
- ad segments
- The SSAI service now:
- Delivering the Stitched Manifest to the Player
- The OTT player receives a normal-looking stream:
- No separate ad requests needed.
- The player simply continues reading segments sequentially.
- No concept of ad break interruptions.
- This is why SSAI has zero buffering between ads and content.
- The OTT player receives a normal-looking stream:
- Player Continues Seamless Playback
- The player experiences:
- no swapping between streams
- no additional HTTP calls
- no UI overlays (unless implemented separately)
- The player experiences:

Advantages of SSAI
- Seamless Playback: Ads are stitched within the content stream, eliminating buffering or latency.
- Ad Blocker Resistive: As the ads are part of the main content, they are not detectable by ad blockers.
- User Experience: Smooth transition between ad and main content ensures view engagement.
Challenges of SSAI:
- Complex Infra: Requires a robust server system and transcoding workflows.
- Limited Tracking: Accurate event tracking is more complex than
SSAI and CSAI Compassion
| Feature | SSAI | CSAI |
| Playback Quality | Smooth and uninterrupted | May experience buffering |
| Ad-Blocker Resistance | High | Low |
| Interactivity | Limited | High |
| Implementation Complexity | Backend intensive | Frontend intensive |
| Tracking Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Best Use Cases | Live streaming, premium OTT platforms | On-demand and mobile-first experiences |
Revolutionizing OTT Advertising with AI
As the content delivery is being personalised increasingly, the ads shall also evolve. With AI, ads can be optimised and delivered across OTT platforms.
- Personalized Ad Targeting: AI analytics can analyse user behaviour, preferences, watch history, and even emotions based on content genre to deliver hyper-personalised ads. Resulting in increasing engagement and revenue.
- Ad Placement: AI systems can identify the optimal points to insert the ads by understanding the content structure and view engagement patterns.
- Ads Optimisation: AI can generate tailored ads based on user region, language, device type, and content genres.
- Adaptive and Contextual Ad Experiences: AI enables real-time adjustments to ad experiences based on viewer engagement, time of day, or device type. For instance:
- Premium subscribers may see fewer yet more valuable ads.
- Younger audiences could experience more interactive or gamified ad formats.
- Shoppable video ads might allow direct integration with e-commerce platforms.
Conclusion
SSAI and CSAI are foundations in OTT advertising, each with its strengths and limitations. SSAI ensures smooth, uninterrupted playback, while CSAI enables detailed tracking and interactivity.
The integration of AI is going to redefine OTT advertising by making it predictive, personalized, and contextually relevant. The future of OTT advertising will focus not only on reaching viewers but engaging them intelligently, creating ad experiences that complement content rather than disrupt it.
Key Takeaway:
The evolution of OTT advertising is moving towards AI-powered hybrid ad delivery, where relevance, seamlessness, and personalisation converge to enhance both monetisation and user experience.

