GA4 vs Universal Analytics: What is the Difference?
With the arrival of Google Analytics 4, there is a new ecosystem in the world of Google Analytics. With the current Google Analytics Universal Analytics firmly established as the most used Analytics platform, it is a challenge for most businesses with existing Universal Analytics setup and also new businesses who want to implement a new analytics platform.
1. Data Model
GA3 uses a data model where user activities are tied to pageviews and sessions. The analytics code fires a pageview cookie that contains other information pieces tied together like browser, Ip location, other demographics like age, gender and user type etc. This pageview hit is the basic building block for calculating other metrics in analytics. These pageviews and sessions are tied to page urls that rely on page loads to send pageview calls.
GA4 employs a different data model using events and parameters. All hits including pageviews and sessions are tracked as events. These events, unlike in the case of Universal Analytics, are not dependent only on pageview calls. They instead can trigger on interactions like clicks, play and pause. Each of these event calls are tied to multiple “Parameters” that send information like timestamp, browser, IP location etc. This mechanism is specifically useful for unified tracking of Web and Mobile applications.
Unlike Universal Analytics, in GA4 one can pass multiple parameters for a single event. In Universal Analytics, there exists a restriction of Category, Action and Label to pass event variables.
2. Event Categories
GA4 has distinct event categories. Not to be confused by the Event Category field within Universal Analytics. The GA4 events are categorized as follows:
- Automatically collected
- Enhanced measurement
- Recommended
- Custom
- Automatically collected: These are events that are triggered automatically as soon as a GA property is created along with a Data Stream. Example:
- first_visit – the first visit to a website or Android instant app
- session_start – the time when a visitor opens a web page or app
- user_engagement – when a session lasts longer than 10 seconds or had 1 or more conversions or had 2 or more page view
- Enhanced measurement: These are automatic events similar to “Automatically Collected” events. The only difference is that these are optional. You need to enable these optional events under the “Enhanced Measurement” option.
- Recommended: As the name suggests, these are events that Google recommends specific to your business. These are not automatically configured but require custom implementation. Eg: ad_impressions when a user sees an ad on your app. Or add_to_cart in case you have an ecommerce platform.
- Custom: These are custom events that fall in none of the above categories. These are events that are very specific to your needs and can be defined completely as per your convenience. Eg: tracking a particular button click for “Registration” or a specific step in a form submission.
- Automatically collected: These are events that are triggered automatically as soon as a GA property is created along with a Data Stream. Example:
Learn more about Event Categories
3. Data Streams
In GA4, each entity that needs to be tracked needs to have a specific data stream. For example, if you have a website and 2 different mobile applications running parallelly. They all need to have distinct “Data Streams”. In this case, there will be three data streams each for the web and two mobile applications. Do not confuse this with Views in Universal Analytics. There are some basic rules that can be applied to each Data Stream but once applied, you cannot toggle between views with different filters as you are able to do in Universal Analytics. For example:
- Set up a list of domains for cross-domain tracking
- Create a set of rules for defining internal traffic rules
- Put together a list of domains to exclude from tracking
Each Data Stream has a distinct Measurement ID that follows the nomenclature G-XX123XX2YZ. Each measurement ID can be set to enable or Disable “Enhance Measurement” Events. Data Streams are primarily used to capture data independently from distinct applications and then tie it to a single property where a relationship between the various collected data is already established using GA4’s Data Model.
Two things to watch out for w.r.t. Data Streams:
- You cannot edit a data stream after it has been created
- Deletion of a data stream cannot be undone

4. Integration of Web and Mobile
Universal Analytics is primarily focused on websites. This is because it was built in a time when desktops were essentially the main channel for online traffic. Hence, this ecosystem was designed primarily for a desktop first UI/UX design which later on was upgraded to allow responsive web designs that are accessible to mobile devices as well. This was due to mobile devices becoming more prominent in bringing online traffic to the web.
GA4 is an ecosystem designed to accommodate the fundamental shift towards a Mobile First UI/UX design due to the increase in penetration of mobile devices across the internet landscape with key businesses also moving over to mobile applications. This surge in mobile traffic has overshadowed desktop traffic by a long way. With GA4, Google attempts to combine the overall traffic from Mobile and Desktop to create a combined view for businesses to get a one stop solution for their analytics data.
5. Data Collection and Sampling Threshold
The universal analytics allows a threshold of 10 million hits per property. This essentially leads to data sampling when this threshold is breached. There do not exist any restrictions in creating events though. Google Bigquery integration is not allowed for free accounts of Universal Analytics. That is only allowed for paid accounts or Google 360 accounts.
In the case of GA4, there exists no sampling threshold on data size. However, there is a restriction of 500 events that can be configured. Also, GA4 allows free integration with BigQuery unlike Universal Analytics where it is allowed only in paid accounts. However, for hosting data on BigQuery, one still needs to pay for its use.
Learn more about Sampling Threshold
6. Property << View Restriction
Google Analytics Universal Analytics allows multiple views to be created within a single property. This allows segmenting of data like restricting properties on data attributes like Region, User Types etc. This allows businesses to segment users in order to moderate access w.r.t. Required data. An example can be that a business may choose their APAC account staff to only view APAC data within a GA view that houses only APAC data. Similarly for EMEA account staff there is another view that houses only EMEA data.
GA4 does not allow multiple views within its ecosystem. This restricts all data that is collected within the property to include everything. Hence, there is a reliance on other independent reporting tools to present that restriction.
This particular feature also signals Google’s push towards enabling organizations to use raw data and build reporting customizations using business intelligence to suit their needs.
7. Machine Learning Algorithm
This is one avenue where GA4 is very futuristic. It offers Data Modeling using Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. These learnings are presented within the interface under “Insights”. In the case of Universal Analytics no such feature is available. That makes Universal Analytics limited in its capacity to deliver insights.
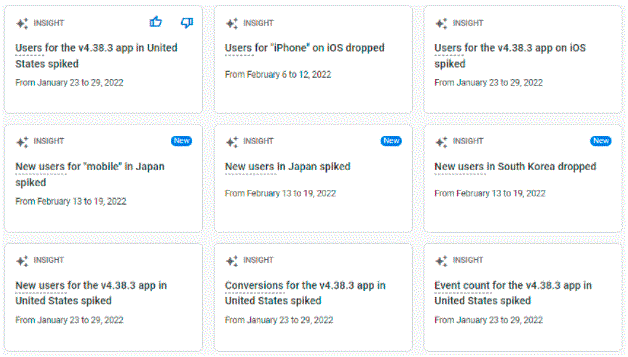
8. Cross Device Tracking
This is another key avenue where GA4 scores over Universal Analytics. Since, the default data model of GA4 is Events and Parameters, this allows all basic metrics like Sessions, Pageviews, Engagement Rate etc to capture information across all devices including mobile devices. Nowadays, user activities are tied to multiple devices as users are frequently switching their devices. Hence, a cross platform that identifies and measures such activities across devices using the same parameters is crucial. An example of this behavior can be a user who views a display campaign on his mobile. Then later on uses his desktop to generate an organic search using the recall by the display ad that he/she viewed earlier.
In Universal Analytics, the default pageview, session metrics are not relevant across multiple devices. Only Events allowed such cross device analytics. This limitation requires workarounds by setting up duplicate events for collecting the same information like page load events which are fundamentally the same as pageviews but are required to be implemented so as to cater to all devices.
Learn more about Cross Device Tracking
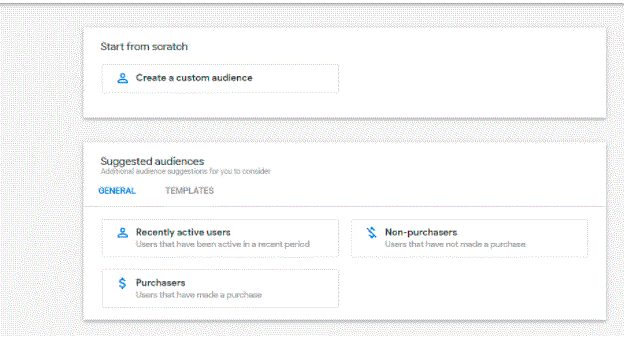
9. Predictive Audience and Metrics
GA4 also provides Predictive Audience capabilities that businesses can use in order to target ads and users who are most likely to purchase your product in the next few days.
The machine learning in GA4 allows you to make future predictions of user behavior in lieu of the campaign goals. This helps you to understand purchasing habits of your clients especially in a cross device environment and helps you formulate campaigns in lieu of such intelligence provided by the platform. In Universal Analytics this feature is missing.
Learn more about Predictive Audience and Metrics
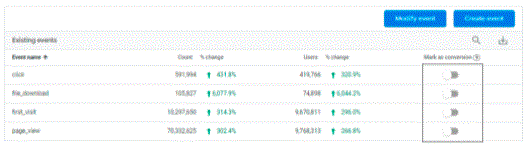
10. Goals vs Conversion Events
In GA4, there are events and specifically you can mark events as Conversion events. These are similar to Goals in Universal Analytics. In Universal Analytics, these Goals need to be configured separately and there is also a limit of 20 goals per view in the free version. In GA4, there are no limits. Also, you do not need to separately create Conversion Events in GA4. You simply need to set existing events by clicking on a toggle switch to enable the event as “conversion”. Similarly, you can click and disable as well.
Learn more about Goals and Conversion events
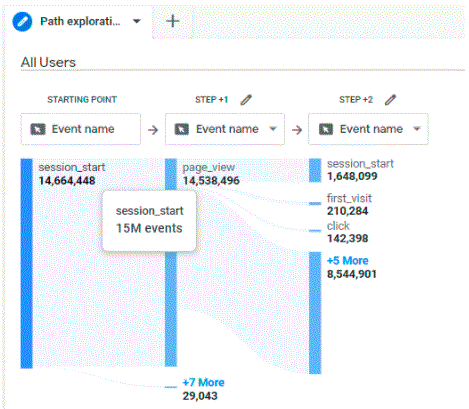
11. Exploration Section
Exploration section is an improvement over Universal Analytics Custom Reports. It is a view which provides in-built templates for your reports that can be tabular, pivots or even charts. It also provides templates for Path Exploration, Funnel Exploration and Free Form. This allows a more in depth analysis of data through charts and visuals that make data consumption easier.
12. Debugview
This is a welcome feature in GA4 that allows you to test your own activity. This feature allows testing by tracking your own activity.
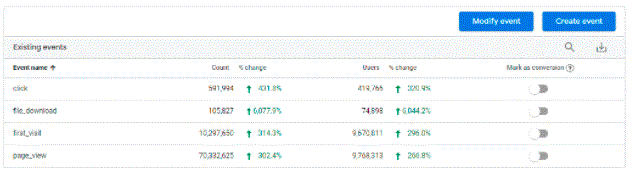
13. Create and modify events
GA4 gives the ability to create custom events within GA4 property itself without any custom configuration. These custom events can be modified as well without any need to write any javascript code in GTM or elsewhere.
Learn more about how to Modify Events
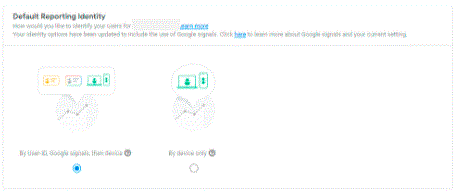
14. User ID Tracking
User ID tracking in GA4 is a lot easier. It only requires opting for an optional feature for enabling User ID tracking.
Based on the above mentioned above, GA4 is a great enhancement for you to incorporate on your website. It provides a new unified landscape for website and mobile apps with less dependence on 1st party cookies. As of now, it has its current limitations as a one stop analytics solution. But it is a great enhancement to Universal Analytics.

