MongoDB Recovery Practice — DR Drill Automation with Terraform, Python & Jenkins
MongoDB Recovery Practice — DR Drill Automation with Terraform, Python & Jenkins
When disaster strikes, the only thing that matters is how fast and reliably you can get your database back. Backups on a shelf are worthless if you can’t restore them under pressure. I built an automated MongoDB restore pipeline with Terraform, Python, and Jenkins so I could repeatedly prove — not just hope — that restores work.
The goal
I set out to remove the tedious, error-prone steps we kept repeating. I wanted a restore flow that was identical across environments, a script to build replica sets so we wouldn’t misconfigure anything by hand, and real validation that proves the data is intact. Centralizing the whole thing in Jenkins meant every run is auditable and repeatable. In the end we built a single pipeline: it provisions infrastructure, applies the backup, runs integrity checks, and stores logs and a validation report for post-mortems and audits.
Result: one pipeline that spins up infra, restores MongoDB from backups, validates the restore, and stores logs and reports.
The workflow
1.,Infrastructure with Terraform
I use Terraform to bring up clean infra for each drill — EC2s (or VMs/containers), networking, and persistent volumes. That guarantees the same starting point every time and removes “works on my machine” surprises.
2.Replica set creation (Python)
Instead of typing rs.initiate() and rs.add() by hand, a Python script does it for me. It handles the ordering and retries so the replica set comes up consistently.
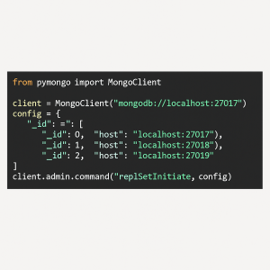
code 1
Automating this avoids timing issues and misconfigurations.
Backup & restore
Backups are normalized into compressed archives. The restore routine unpacks a dump and applies it to the freshly provisioned MongoDB nodes, following the automated replica set setup.

Image 2 :
dump creation
Restoration executes through:

Image 3
restoration initate
4.Validation & comparison
This is the real game-changer. Rather than hoping the restore worked, I run a validation script that:
checks what collections exist (and whether any are missing),
compares document counts collection-by-collection,
compares indexes,
optionally samples _id values for obvious mismatches.
If counts and indexes match, the script returns success (exit code 0); if not, it fails. That makes it perfect for CI/CD — Jenkins can gate the pipeline on the validation result.
5.Logging & reporting
Every step logs to Jenkins. The validation creates a structured JSON report and Jenkins archives logs and artifacts for audits. That audit trail builds trust: when auditors ask, you can show a drill’s inputs, outputs, and validation report.
6. Jenkins orchestration
Single Jenkins job with stages:
Terraform → Replica Set Setup → Restore → Validation & Comparison → Archive Logs
Image 3 :
Flow diagram

Pipeline Sample
Lessons learned
Automate infra and DB setup. Terraform gives you a clean slate for every run and removes manual variability.
Validation is not optional. Counts and index checks catch a lot of issues you wouldn’t notice otherwise.
Logs equal trust. Storing artifacts in Jenkins makes your drills credible to others.
Practice makes perfect. Each drill gave me small improvements to scripts and timing.
Minimal input reduces errors. I trimmed the required inputs to just host + DB name and let scripts infer the rest.
Outcome
Now a single Jenkins job can provision infra, build a MongoDB replica set, restore from dumps, validate data and indexes, and store the whole run as an auditable artifact. The drills are predictable, repeatable, and quick — the kind of confidence you actually want during an incident.
Drills are predictable, repeatable, and fast — the confidence you want during an incident.
Restoration drills were made predictable, quick, and reliable
Appendix—Validation script (summary)
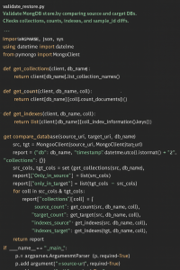
alidate_restore_optimized sample code
Returns exit code 0 when counts and indexes match.
Returns non-zero on mismatch so Jenkins can fail the build.
Produces a JSON report with collection names, counts, index diffs, and sample _id checks.
Usage
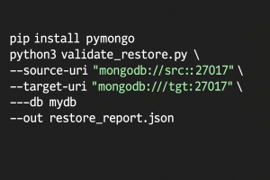
Compare output example code
This script returns 0 in case of success (counts + indexes equal), or a non-zero value if mismatches occur — which makes it perfect for Jenkins pipelines.
Final takeaway
Backups don’t save you — restores do. Automating the infra, the replica set, the restore, and the validation turned a slow, error-prone task into a single-click procedure you can trust. If you run MongoDB in production, drill restores until you can do them under pressure — that’s when you’ll know your backups are actually useful.

